AMD Radeon R7 240GB SSD review
3. HDTachRW, HD Tune Pro
Here is our testbed:
- Shuttle SH81R4
Processor: Intel i7 4790Graphics card: Club3D Radeon HD 6790 CoolStream EditionMemory: 2x8GB RAM DDR3-1600 CrucialSSD: 512GB Crucial MX100Monitor: LG L246WH-BH 24" - Windows 7 x64 SP1 with latest updates installed
For the tests, we used the following software:
- HDTachRW v3.0.1.0HD Tune v4.50 ProCrystal DiskMark v3ATTO Disk Benchmark v2.46 ASS SSD Benchmark 1.5xxxIOMeter v2006.07.27 with Xtreme Benchmark templatePCMark Professional edition v1.04
- Anvil Storage Utilities 1.0.34. Beta 11
We start the tests with the HDTachRW software. The software measures the sequential read speed, the random access speed and sequential write speed. Remember that the HDTachRW feeds the tested drive a continuous string of small sequential requests. It doesn't equate to real-world maximum throughput, but it does mean something for analysis.
In this benchnark, the AMD drive had the same behavior with the OCZ ARC 100 SSD. Although the reading speed was consistent throughout the SSD at 318MB/s (average),, the writing speed dropped to about 220 MB/s at around the 137 GB mark and remained at these levels until the end of the sequential write benchmark.

We move on to the HD Tune Pro software, another utility we used to measure the drive's reading and writing performances. Although not necessarily representative of real-world workloads, HD Tune's targeted tests give us a glimpse of each drive's raw capabilities.
This time the sequential reading test returned a 252.2MB/s average speed:

As you see in the screenshot below, the graph below is not smooth and the average write speed was was 300MB/s.
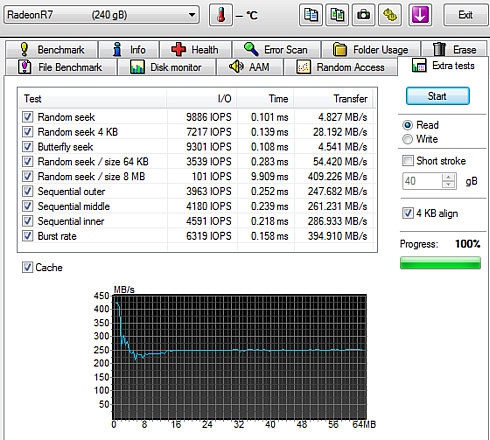
Below you see random reading test, where the AMD Radeon R7 SSD gave a 340.6 MB/s average reading speed for an 1MB transfer size and a 2992 MB/s average reading for transferring files with random sizes - a decent performance.
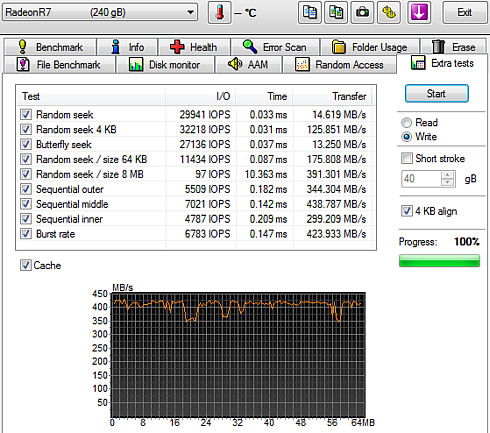
In the corresponding random write test, the SSD wrote files with random sized at 422.903 MB/s and 1MB files a little faster, at 467 MB/s. Smaller 4KB files were written at 142.37 MB/s. The results for those small random writes are impressive.

HD Tune's file benchmark consists of two parts: the transfer speed test and block size test. The transfer rate test measures three different parameters for both reading and writing:
- Sequential: the sequential speed is measured and shown on the graph. Ideally the transfer speed line should be straight and smooth.
- 4 KB random single: this test measures the performance of I/O operations of 4096 byte blocks - the most common I/O operation on a typical system. Especially the 4 KB write speed is an important indication of general system performance.
- 4 KB random multi: this test is similar to the 4 KB random single test except that multiple requests are sent simultaneously to the device. We set the number of operations to 32.
HD Tune's file benchmark also features three data patterns available that can be used during the write process: zero, random and mixed, which is a combination of zeroes and random data. Certain SSDs use a compression technique which improves performance when compressible data is used. For these devices the results will be highest when writing zeroes and lowest when writing random data.
Let's start with a sequential transfer speed of a 500MB file using zeros in the writing part:
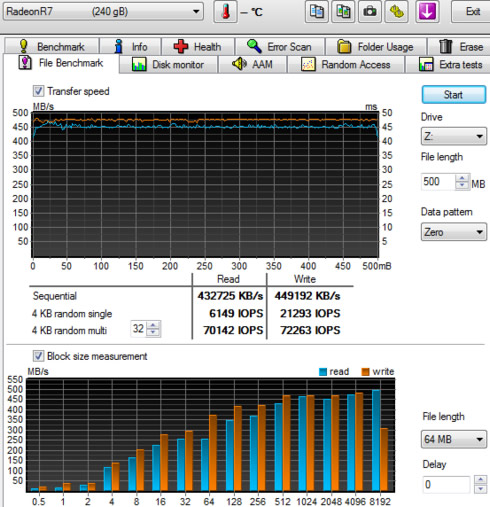
The AMD Radeon R7 SSD read the 500MB file at an average speed of 432.7 MB/s and wrote the file at 449.2 MB/s, which is good in both cases. The 4K random single performance with 4096 byte blocks was 6149 IOPS for reading and 21293 IOPS for writing, which are also high. When we enabled the 32 requests option, both figures were boosted up to 70142 IOPS and 72263 IOPS for both read/write, respectively.
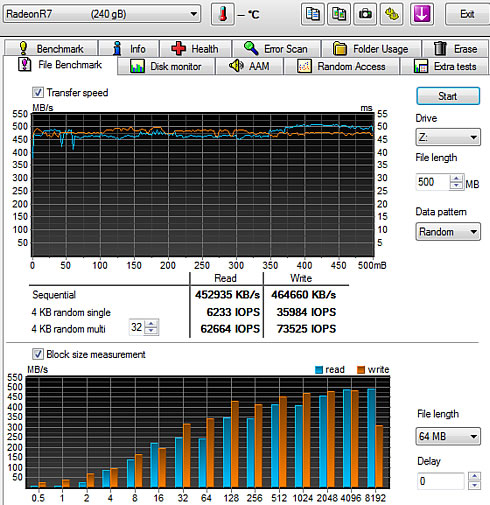
Selecting the "Random" data pattern (zeroes and data) did not have any significant impact to drive's sequential read performance:
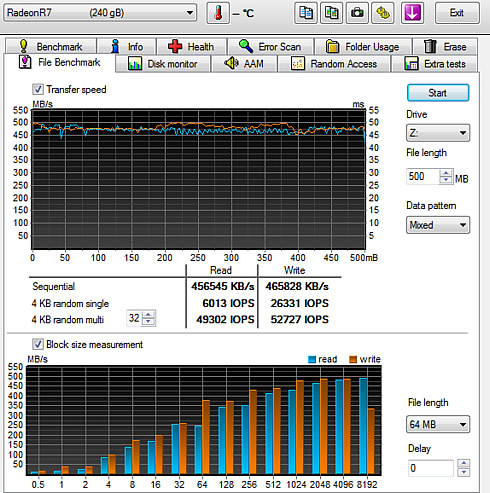
The reading result with a "mixed" data pattern was a bit slower mainly in the 4KB random multi 32 test:
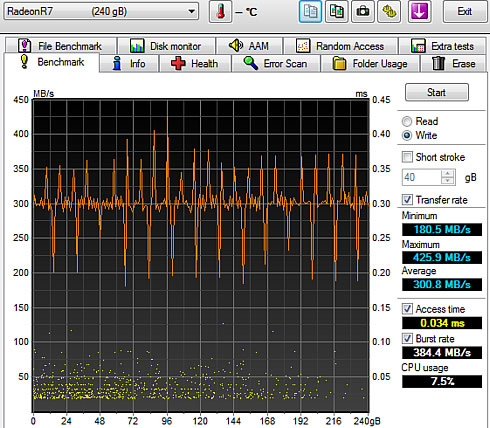
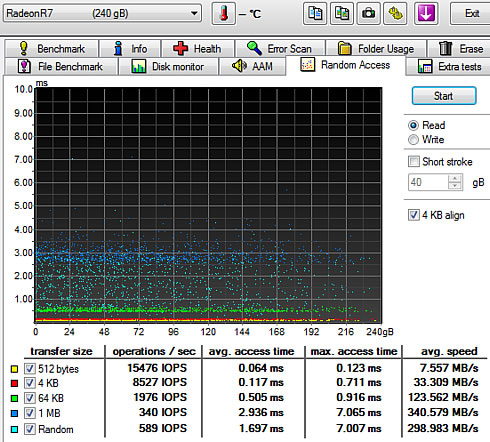
Below you see some additional sequential and random reading and writing tests: