FCC Authorizes SpaceX to Provide Broadband Satellite Services
The Federal Communications Commission approved an application by SpaceX to provide broadband services using satellite technology in the United States and around the world.
The Federal Communications Commission approved an application by SpaceX to provide broadband services using satellite technology in the United States and around the world.
This is the first approval of a U.S.-licensed satellite constellation to provide broadband services using a new generation of low-Earth orbit satellite technologies. SpaceX proposed a satellite system comprised of 4,425 satellites and was granted authority to use frequencies in the Ka (20/30 GHz) and Ku (11/14 GHz) bands to provide global Internet connectivity.
The authorization outlines the conditions under which SpaceX is authorized to provide service using its proposed NGSO FSS satellite constellation.
Over the past year, the FCC has approved requests by OneWeb, Space Norway, and Telesat toaccess the United States market to provide broadband services using satellite technology that
holds promise to expand Internet access, particularly in remote and rural areas across the country.
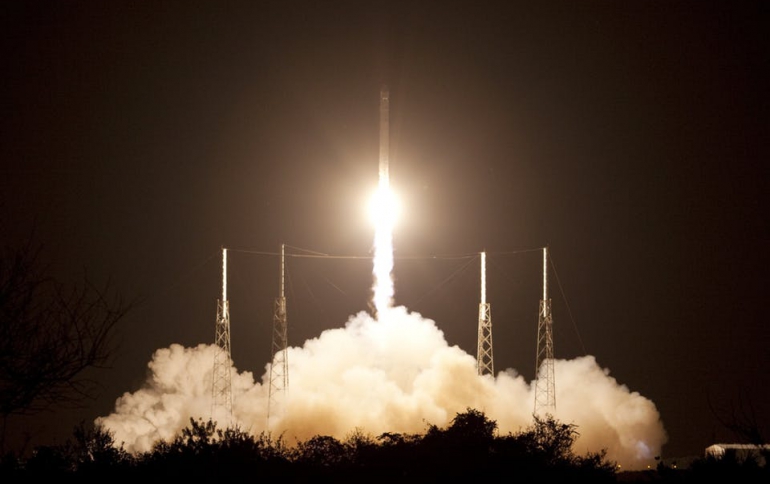
Succesful launch of Iridium Satellites
In related news, Space Exploration Technologies Corp. launched a rocket carrying 10 Iridium Communications Inc. satellites to orbit early Friday, its fifth in a series of eight launches contracted for the communications company as it builds its NEXT constellation network.
The Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from Vandenberg Air Force Base on California's central coast at around 7:13 a.m. local time. SpaceX has signed on to deliver 75 Iridium satellites to orbit in total. SpaceX said on Twitter about an hour after launch that all 10 satellites had been deployed.
Friday's launch used the same first-stage rocket from Iridium's similar mission in October.