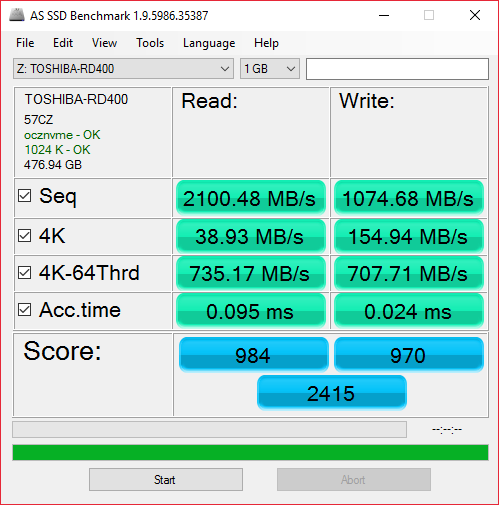
Toshiba OCZ RD400 512GB M.2 PCIe SSD
5. AS SSD benchmark
We move on with the AS SSD benchmark, which contains five synthetic as well as three practical tests. The synthetic tests determine the sequential and the random read / write performance of an SSD. These tests are carried out without using the operating system's cache. The Seq-test measures how long it takes to read and write an 1GB file. Most importantly, this sequential benchmark uses incompressible data for all of its transfers.
The OCZ RD400 SSD 960GB SSD reached a very high score of of 2415. That's a bit short of the 2848 score of the Samsung 950 Pro SSD, which had an overall lead in the read tasks.
Sequential speeds for Toshiba's drive hit the 2100MB/s for reads and 1074MB/s write while 4K speeds reached 38.93MB/s for read and 155MB/s for write.

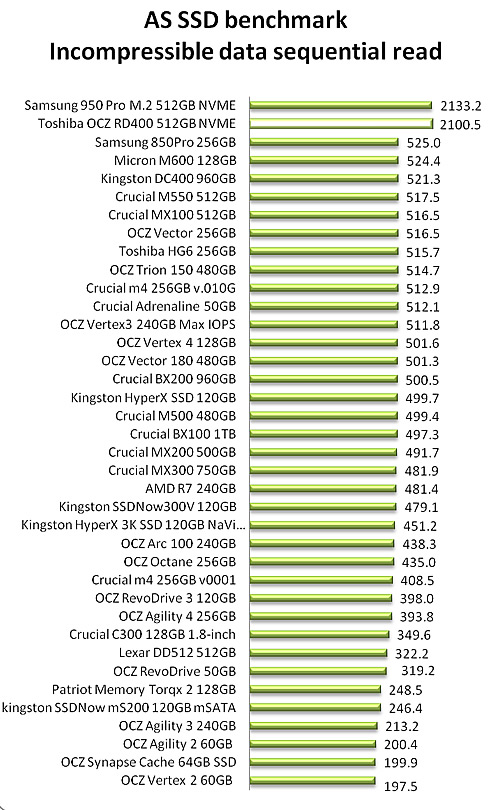
The RD400 goes head to head with the 950Pro in the sequential read test:
Toshiba's drive lost some ground in the 4K random read tests, especially in the multithreaded test, finishing second in the following charts:


The performance for the RD400 SSD in the sequential write test was high, although not higher than the 950 Pro's.

Once again, both the RD400 and the 950 Pro drives had the same performance in the 4K random write test, but Samsung;s drive showed its muscles in the 4K/64 thread write benchmark:


Next up we ran the Compression Benchmark built-into AS SSD. This test uses a mix of compressible and incompressible data and outputs both Read and Write throughput of the drive.
The Toshiba RD400 SSD showed an unstable behavior across the board, with significant dips of many MB/s in the read test, mainly after the 60% compressibility mark on the chart below. Writing was also faster after the same 60% mark and onwards:






















