New ARM Mali-470 GPU Offers Improved Efficiency On Wearable and IoT Devices
ARM has released a new efficient graphics processing unit (GPU) to enable smartphone-quality visuals on wearable and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The ARM Mali-470 GPU delivers an enhanced user interface for power-constrained products, including smart watches, home gateways and appliances, industrial control panels and healthcare monitors. It is available for immediate licensing, with the first Mali-470 enabled devices expected in late 2016.
Mali-470 delivers the same performance of the Mali-400 while halving the power consumption at the same process geometry. Power gating has been extensively used to shut off transistors when they’re not needed, and also clock gating use has been improved when power gating isn’t an option.
In addition, Mali-470’s vertex processor has been optimized to better handle fixed-point arithmetic. The pixel/fragment processor on the other hand has not gone untouched, with ARM working to cut down on the amount of time spent by the fragment processors changing between states.
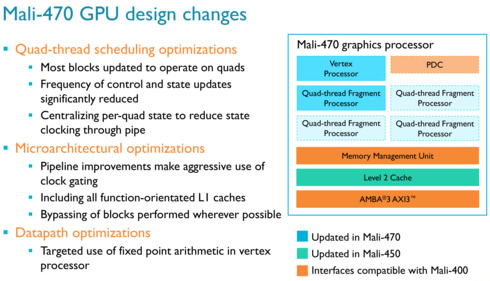
Its die area is 10 percent smaller than Mali-400 and delivers optimal energy efficiency for screen resolutions up to 640x640 in single-core configurations and higher resolutions for multi-core configurations.
In addition, the Mali-470 offers increased frame rates and can be used as building block of optimized SoCs for power-constrained devices when paired with the low-power ARM Cortex-A7 or Cortex-A53 processors.
The majority of Android, Android Wear and other emerging operating systems use the OpenGL ES 2.0 API and driver stack. Mali-470 uses the same OpenGL ES 2.0 driver stack as Mali-400 so there is no need to re-optimize existing applications.