Corsair CM2X512-8000UL
5. Performance Test v5.0
Review Pages
- Memory Benchmarks
This suite contains a number of tests that exercise the memory sub-system of the computer. (Random Access Memory- RAM)
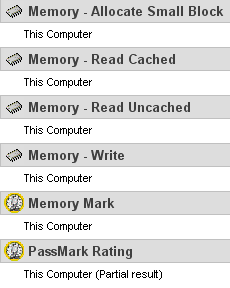
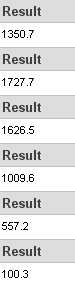
Memory - Allocate small block
This test measures the time taken to allocate & free small zeroed memory blocks (around 100KB block size)
Memory - Cached
This test measures the time taken to read a small block of memory. The block is small enough to be held entirely in cache (if one is present)
Memory - UnCached
This test measures the time taken to read a large block of memory. The block is too large to be held in cache.
Memory - Write
This test measures the time taken to write information into memory.
| 667MHz | 800MHz | 1000MHz | |
 |
 |
 |
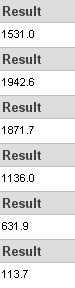 |
According to Passmark the difference in performance was greater when stepping up from 667MHz to 800MHz than from 800MHz to 1000MHz. In most cases, the reported results were similar for Corsair when running at 800MHz and 1000MHz.
- Advanced Memory Benchmark
Memory Speed Per Access Step Size
The first test type, ‘Memory Speed Per Access Step Size’ accesses a large block, of memory in various sized steps. First, it runs through the block of memory sequentially, accessing every value. Next it runs through the same block again, except this time it accesses every second value. On this occasion, it runs through the block twice in order to access the same amount of data as the initial step. Next it runs through the same block again, except this time it accesses every fourth value and so makes four passes. And so on, until a certain maximum step size is reached.
The size of the block of memory used for this test is one quarter the amount of system RAM. The size of the steps varies from 1 (continuous sequential access), to one quarter the size of the block of memory ( i.e. one sixteenth of the system RAM ).
| Memory Speed (MB/Sec. per Step Size) | 667MHz | 800MHz | 1000MHz |
| Block Read Speed | 41.76 | 43.88 | 46.62 |
| Block Write Speed | 27.80 | 27.24 | 31.56 |
| Click on the links above for the full graphs | |||
According to the specific test, there is a great difference between the three setups.
Memory Speed Per Block Size
When a computer program wants to use a section of memory to store data, it makes a request to Windows for the amount of memory it requires. Windows allocates the memory to the program ( unless system resources are very low ) and returns to the requesting program the address of the first memory slot in the allocated block. It is possible that some programs may request very large amounts of memory. The ‘Memory Speed Per Block Size’ test like the ‘Memory Speed Per Access Step Size’ test, is composed of many steps. During each step of the test, PerformanceTest requests a block of memory and runs through the block measuring the average access time. However on each subsequent step the size of the requested memory is increased, until finally a block close to the size of the system RAM is requested. In this way it is possible to observe the different access speeds for the different sizes of blocks.
Typically it is possible to see very fast memory access for blocks which are small enough to fit entirely into the L2 RAM cache, and slower access times for larger blocks accessed from main RAM. In the case where system resources are low, swapping to the disk may even be required for very large blocks.
| Memory Speed (MB/Sec. per Block Size) | 667MHz | 800MHz | 1000MHz |
| Block Read Speed | 430.86 | 484.12 | 485.33 |
| Block Write Speed | 298.91 | 335.75 | 336.33 |
| Click on the links above for the full graphs | |||
On the other hand, the memory speed when measured per Block size reported near similar performances at 800MHz and 1000MHz.
Review Pages