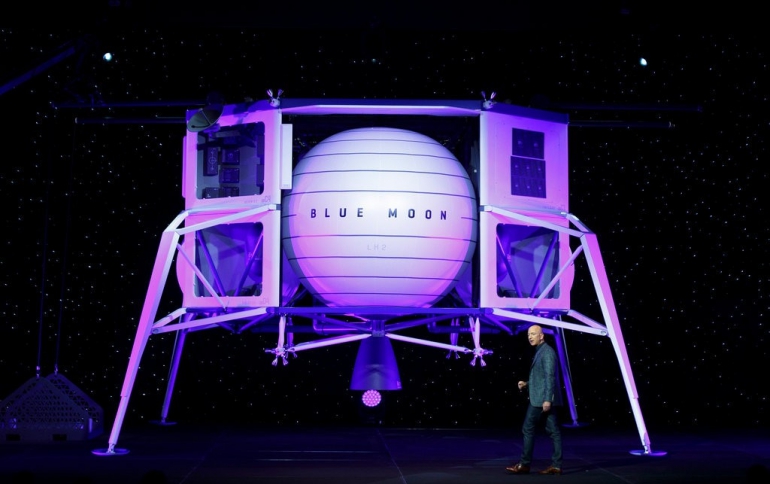

Jeff Bezos Unveils Blue Origin’s Lunar Lander Blue Moon
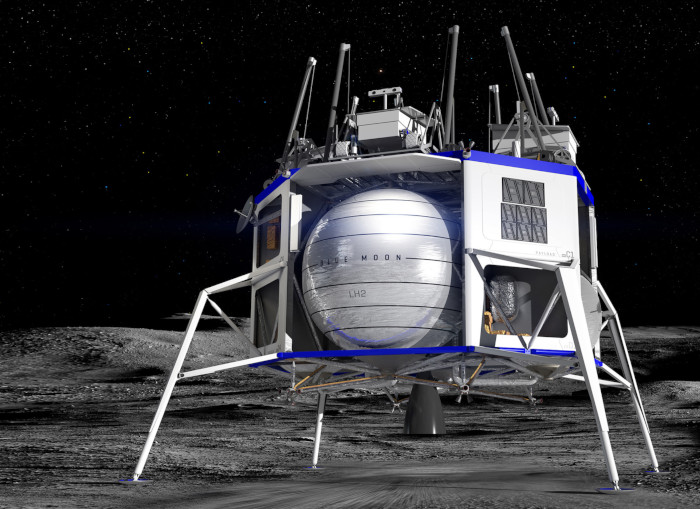
Jeff Bezos, founder of Blue Origin and Amazon, today unveiled the design of his spaceflight company’s lunar lander, the Blue Moon, which can take scientific payloads and humans o the surface of the Moon.
“This is an incredible vehicle, and it’s going to the Moon,” Bezos said after unveiling a mock-up of the Blue Moon lander at the Washington, DC Convention Center.
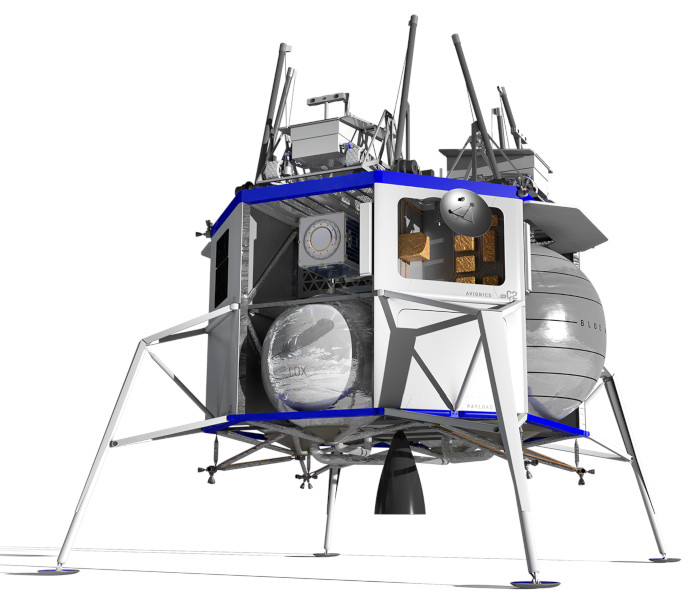
Blue Moon is a flexible lander delivering a wide variety of small, medium and large payloads to the lunar surface. Its technology builds on Blue Origin's experience with New Shepard with respect to LH2/LOX propulsion, precision guidance, vertical landing and landing gear systems.
The top deck and lower bays easily accommodate a wide variety of payloads, including large payloads and ESPA-class payloads with standard ring port interfaces. There are lower mounting locations for payloads, useful for closer access to the lunar surface and off-loading.
The Blue Moon lander provides kilowatts of power to payloads using its fuel cells, allowing for long mission durations and the ability to last through the lunar night.
The larger variant of Blue Moon has been designed to land an ascent vehicle that will allow Blue Origin to return Americans to the Moon by 2024, according to Bezos.
Bezos said that the company will conduct its first ignition test this summer.
“One of the most important things we know about the Moon today is that there’s water there,” Bezos said. “It’s in the form of ice. It’s in the permanently shadowed craters on the poles of the Moon, and water is an incredibly valuable resource.”
“We’re using liquid hydrogen is because, ultimately, we’re going to be able to get hydrogen from that water on the Moon and be able to refuel these vehicles on the surface of the Moon,” Bezos said.

Bezos also said he would like to see the creation of ‘O’Neill cylinders’ or giant space stations with artificial gravity, capable of holding millions of people or entire landscapes in space.
Blue Origin received $13 million from NASA to work on technologies needed for a moon lander.
NASA is aiming to explore craters near the moon’s South Pole where water ice is believed to exist. The water molecules can be broken apart into hydrogen and oxygen, which could be used for rocket fuel. The resources would also be handy for astronauts — water for drinking, oxygen for breathing.
Bezos founded his rocket company in 2000, which means that it has been around longer than the other, better-known billionaire rocket company, Elon Musk’s SpaceX. Musk started SpaceX in 2002.
Last year, SpaceX announced that a Japanese billionaire, Yusaku Maezawa, had signed up for a trip that would go past the moon without landing on it, and swing back to Earth.





















