Sony SCD-XB790 SACD Player
2. The Super Audio CD Format
Review Pages
2. The Super Audio CD Format
3. Unpacking
4. Control Menu
5. Reading Tests
6. Error Correction Tests
7. Conclusion
Sony SCD-XB790 SACD Player - Page 2
The Super Audio CD Format
Super Audio CD is the most fundamental improvement in digital music reproduction since the CD itself. No surprise. It comes from the people who invented the CD: Sony and Philips.
Direct Stream Digital™ encoding
Other digital systems—including the very latest designs—use Pulse Code
Modulation (PCM). Unfortunately, PCM record/playback systems require
decimation and interpolation filters that can cause problems, including
requantization noise, passband ripple and ringing. These degradations can
smear musical overtones, muddy the soundstage and compromise overall
transparency. Simply increasing the PCM word length to 24 bits or increasing
the PCM sampling rate to 96 kHz does nothing to overcome these fundamental
problems.

Compared to CD, Super Audio CD is far simpler. Super Audio CD
eliminates decimation and interpolation filters.

Direct Stream Digital™ process (bottom) is far simpler than
the PCM digital process (top).
DSD uses 1-bit delta-sigma modulation and a sampling frequency 64x higher than CD. Super Audio CD recordings don't have to subject the original sound waves to the decimation and interpolation stages associated with PCM. Hence DSD sound reproduction is much more natural and accurate in staging and is often favourably compared with the best analogue recordings, but without the hiss and other artifacts that are also associated with analogue recordings. Sony's 1-bit system encodes music at an astonishing 2,822,400 samples per second.
Super Audio CD data is stored on the same physical carrier as DVD-Video. Making use of this highly successful consumer product brings many advantages, such as the use of mass produced components and making combination players which play both SA-CD and DVD-V.
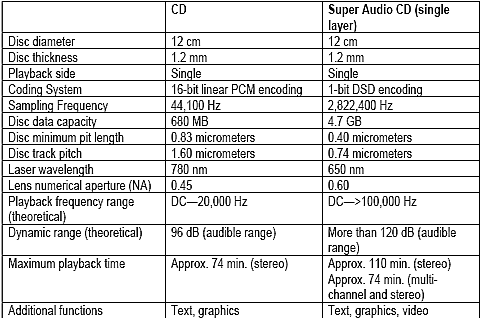
This silver disc can store more than seven times the information of the standard CD, providing up to 74 minutes of full resolution surround music – the same duration as a stereo CD. A Super Audio CD has two distinct mixes, one for stereo and one for multi-channel.
DSD: the recording technology behind SA-CDSuper Audio CD uses a new and radically different technology called Direct Stream Digital (DSD) to convert music into a digital signal that can be stored on a disc. Compared to the traditional PCM method (the technology used for CD), DSD offers a much higher resolution by following more closely the original wave form of the music. With a frequency response of over 100kHz and a dynamic range over 120dB across the audible frequency range – some 64 times higher resolution than CD - Super Audio CD offers music reproduction that reveals details you just can’t hear on a normal CD.
The Direct Stream Digital™ pulse train "looks" remarkably like the analog waveform it represents. More pulses point up as the wave goes positive and down as the wave goes negative.
Thanks to DSD encoding, the Super Audio CD format offers frequency response up to 100 kHz and a theoretical dynamic range of more than 120 dB. But specifications alone cannot express the advantages of DSD. DSD one-bit encoding strips away entire classes of distortion that have always characterized PCM. The DSD system provides nothing less than a quantum leap in music resolution.
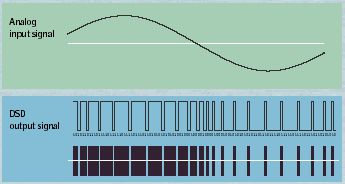
The DSD pulse train "looks" remarkably like the analog waveform it
represents. More pulses point up as the wave goes positive and down
as the wave goes negative.
Multi-channel Super Audio CD
Producers also have the option of creating multi-channel Super Audio CDs
that can transport you to the acoustic space of the original recording. You'll hear
the most convincing soundstage ever presented at home. Super Audio CD multichannel
sound is based on the international standard ITU-R speaker setup. So
it's directly compatible with many of today's home theatre speaker systems.
For full compatibility with pure stereo Super Audio CD players, every multichannel
Super Audio CD includes a complete stereo rendition from the hand of
the producer. You're never at the mercy of a computerized "fold-down" of the
multi-channel mix. You'll always hear the producer's original intent.

Super Audio CD multi-channel sound is based on the international ITUR
standard.
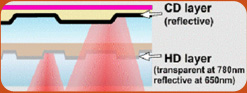
- Hybrid Disc
Furthermore, there is an option to add a separate CD layer to the DVD disc: the so called ‘Hybrid Super Audio CD'. Hybrid SA-CD’s can be played back on virtually all CD drives and players as well as all standard DVD-Video systems. This makes Super Audio CD’s compatible with all the 11 billion CD and DVD players used around the world.


Every multi-channel Super Audio CD includes a separate 2-channel
stereo mix, done by the hand of the producer—not by a computer.
There are four different SA-CD configurations commercially available to record companies:
- Hybrid Discs
 The vast majority of SA-CD’s introduced on the market today are hybrid type, containing the CD layer. This disc plays on a CD and DVD player, at CD quality.
The vast majority of SA-CD’s introduced on the market today are hybrid type, containing the CD layer. This disc plays on a CD and DVD player, at CD quality.
- Single Layer Discs
 There are also SA-CDs without the CD layer, so-called single layer discs. These cannot be played on a standard CD player. The advantage is that this is an entirely secure digital carrier.
There are also SA-CDs without the CD layer, so-called single layer discs. These cannot be played on a standard CD player. The advantage is that this is an entirely secure digital carrier.
Both the hybrid and single layer SA-CD can be released as a stereo-only album, or as a stereo plus surround album.

Super Audio CD offers the world’s most secure digital carrier, utilising a combination of physical and electronic protection barriers. These are layered around the audio content in five independent layers, including a combination of mechanical and encryption-based protection systems that cannot be broken using any current hacking technique.
The end result is that when you buy a Super Audio CD in a music store, you can be confident that it’s the genuine article and not an illegal, inferior quality copy.
The CD layer on the hybrid disc is similar to a conventional CD in that it’s open to copying onto other carriers for home use.
Review Pages
2. The Super Audio CD Format
3. Unpacking
4. Control Menu
5. Reading Tests
6. Error Correction Tests
7. Conclusion