Thermaltake Max4
3. Performance
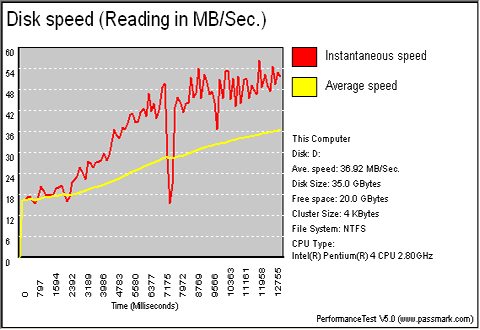
 Passmark Performance Test is an award winning PC hardware benchmark utility that allows everybody to quickly assess the performance of their computer and compare it to a number of standard 'baseline' computer systems. Twenty seven standard benchmark tests are available in seven test suites plus there are five advanced testing windows for custom benchmarking. CPU Tests, 2D Graphics Tests, 3D Graphics Tests, Disk Tests, Memory Tests and CD/DVD Tests. In our case we selected the Disk suite Tests.
Passmark Performance Test is an award winning PC hardware benchmark utility that allows everybody to quickly assess the performance of their computer and compare it to a number of standard 'baseline' computer systems. Twenty seven standard benchmark tests are available in seven test suites plus there are five advanced testing windows for custom benchmarking. CPU Tests, 2D Graphics Tests, 3D Graphics Tests, Disk Tests, Memory Tests and CD/DVD Tests. In our case we selected the Disk suite Tests.
Passmark Disk Test
This suite contains a number of tests that exercise the mass storage units (hard disk or otherwise) connected to the computer. By default drive C: is used but this can be changed from the Preferences Dialog.
For each test a file is created in the root directory of the selected disk. The file size needs to be large in order to get an accurate measurement. In the case where a slow drive is used on a computer with a large amount of RAM this test can take some minutes to complete.
There are a few issues to aware of when interpreting the results of the disk test. These are covered in the precautions section.
- Disk Sequential Cached Read
A large test file is created on the disk under test. The size of this test file is proportional to the amount of RAM available, which stops the entire file from being cached in RAM. The file is read sequentially from start to end. The amount of data read in each individual read operation is always 16KB
- Disk Sequential Cached Write
A large file is written to the disk under test. The size of this test file is proportional to the amount of RAM available. This stops the entire file being cached in RAM. The file is written sequentially from start to end. The amount of data written in each individual operation is always 16KB
- Disk Random cached Seek RW
A large test file is created on the disk under test. The size of this test file is proportional to the amount of RAM available, this stops the entire file being cached in RAM. The file is read randomly; a seek is performed to move the file pointer to a random position in the file, a 16KB block is read or written then another seek is performed. The amount of data actually transferred is highly dependent on the disk seek time.
| HDD | IDE |
Max4 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| HDD on IDE |
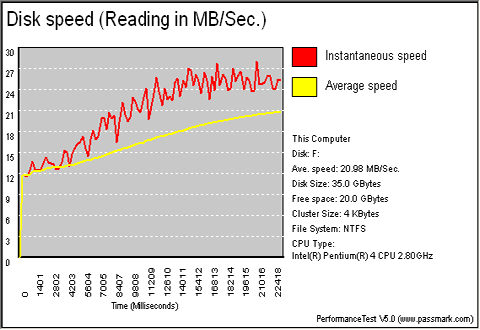 |
| HDD on Max4 |
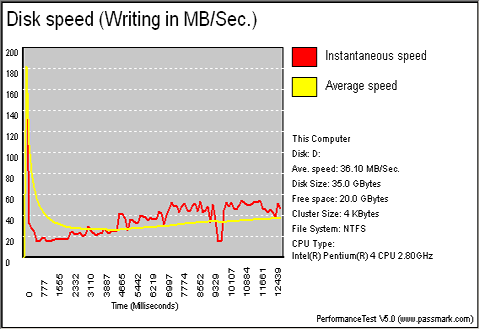 |
| HDD on IDE |
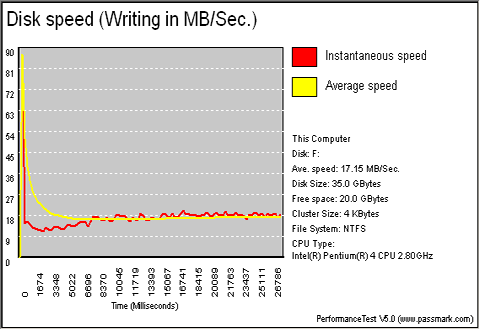 |
| HDD on Max 4 |
Almost double performance when the HD is connected on the motherboard.
| CD/DVD | IDE |
Max4 |
 |
 |
 |
Unlike the HD, the drive reported almost the same performance either connected to the motherboard or as an external in the Ma4 enclosure.
 SiSoftware Sandra is a 32 and 64-bit Windows system analyzer that includes benchmarking, testing and listing modules. It tries to go beyond other utilities to show you more of what is really going on under the hood so you draw comparisons at both a high and low-level in a single product.
SiSoftware Sandra is a 32 and 64-bit Windows system analyzer that includes benchmarking, testing and listing modules. It tries to go beyond other utilities to show you more of what is really going on under the hood so you draw comparisons at both a high and low-level in a single product.
You can get information about the CPU, chipset, video adapter, ports, printers, sound card, memory, network, Windows internals, AGP, ODBC Connections, USB2, Firewire etc. You can save/print/fax/e-mail/post/upload or insert into ADO/ODBC databases reports in text, HTML, XML, SMS/DMI or RPT format.
This version supports multiple sources of information gathering including: remote computers, PDAs, Smart Phones, ADO/ODBC databases or saved system reports. All benchmarks are optimized for both SMP & SMT (Hyper-Threading), up to 32/64 CPUs depending on the platform.
File system Benchmark
- The "File system" which tests how your drive(s) and controller(s) compare to other devices in a typical system:
· Read Test: Buffered, Random, Sequential
· Write Test: Buffered, Random, Sequential
· Seek Test
The "Drive Index" mark is a composite figure representing an overall performance rating based on the average of the read, write, and seek tests, and file and cache size. The Drive Index is intended to represent drive performance under typical use in a PC. A larger number means better performance. The weighting of the results is not equal and represents the distribution of different files sizes as used on these devices (obtained through field research).
| File system Benchmark | |
| HDD on IDE | |
| HDD on Max4 | |
The HDD device performed better connected on the motherboard, with almost double the performance to the same HDD on the Max4 enclosure.
Removable Storage/Flash Benchmark
- The "Compact Flash" typical usage model for these devices is File operations, such as Writing a file to the device, reading a file from it, and deleting a file. This benchmark exercises the devices in terms of these operations (to measure the “raw” cluster level performance of the device, it is recommended to also test it by means of the File System Benchmark module). The following characteristics are measured for each of the four representative file sizes of 512 Bytes (representing a minimal single data cluster file), 32kB, 256kB and 2MB. The weighting of the results is not equal and it represents the distribution of different files sizes as used on these devices (obtained through field research). For each of the four file sizes, a Combined Index is then calculated, stating the combined performance in terms of Combined Operations Per Second, with respect to a mix of write, read and delete operations.
- Combined Device Index: is a composite figure representing an overall performance rating based on the average of the Combined Index figures over the four file sizes. (Higher is better, i.e. better performance)
- Endurance Factor: is a figure representing the Wear and Life Expectancy of flash devices; this is obtained by dividing the average performance (normal condition, i.e. sequential write) to the lowest performance (high-stress condition, i.e. same block re-write). It measures the relative improvement of endurance caused by the wear leveling or flash management algorithm; the absolute endurance of a device (i.e. its expected life-time) is directly dependent, in addition to this Endurance Factor, on the nominal manufacturer rating of maximum erase/reprogram cycles, which is typically 100,000+ for SLC and 10,000+ for MLC devices. (Higher is better, i.e. longer life-time for the device)
| Removable Storage/Flash Benchmark | |
| HDD on IDE | |
| HDD on Max4 | |
Once more, as expected, the HDD on M/B IDE performed better than the Max4 enclosure. Note also, that the Endurance factor for the HDD when put normally under the standard IDE interface is increased in comparison to the Max4 endurance factor.
CD-ROM/DVD Benchmark
Tests how your CD-ROM/DVD drive and controller compares to other CD-ROM/DVD drives in a typical system:
- Read Test: Buffered, Random, Sequential
- Seek Test
This benchmark consists of 2 different tests:
- Data CD performance
- DVD performance
For these tests, the Sandra Test CD/DVD disks are recommended that contain the optimum data files. You can also make a compatible test CD/DVD by burning one with a file of 1/3 disk capacity in the root and similar size files that fill the CD.
CD/DVD Drive Index: is a composite figure representing an overall performance rating based on the average of the read, write, and seek tests, and file and cache size. The CD/DVD Drive Index is intended to represent drive performance under typical use in a PC. A larger number means better performance. The weighting of the results is not equal it represents the distribution of different files sizes as used on these devices (obtained through field research).
CD-ROM/DVD Benchmark DVD on IDE DVD on Max4
The DVD performance in both cases reported equal results, with a drive index of 5MB/s for both the IDE and Max4 interfaces.
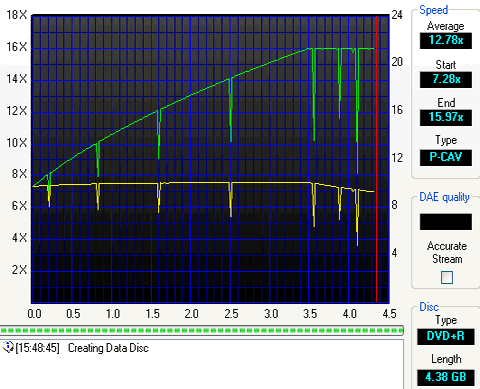
The final test we did was a simple transfer rate reading test with Nero's CDSpeed.
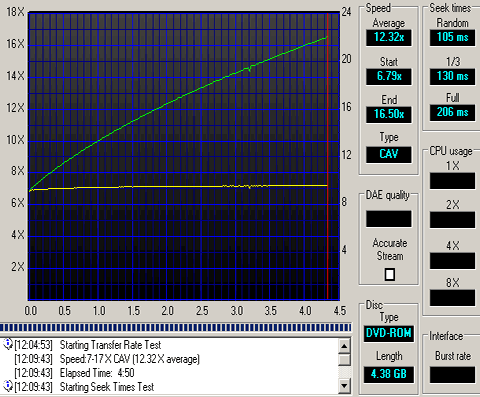
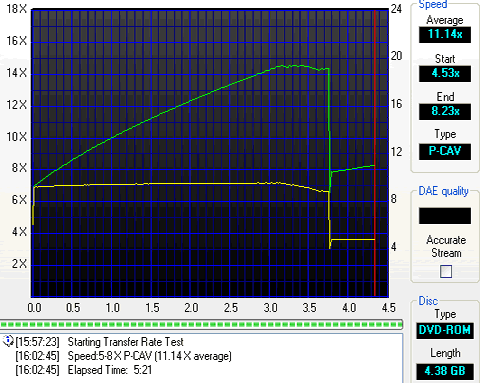
The reading started at the same speed there were differences at the end when using the Max4. When the drive was connected on the motherboard the reading graph was smooth with any single speed drop. In case of Max4 and USB2.0 interface it seems that the drive failed to reach its maximum reading speed of 16X. Over 14X the drive lower its speed down to 8X. When it comes in reading this is not a great issue but in case of recording might the process might fail. We used the "Create Data Disc" feature of CDSpeed and fortunately we didn't notice any speed drop, apart from those of the drive's writing strategy.