ARM Discloses 64-bit Architecture For Servers, TSMC Outlines Logic Technology Roadmap
ARM has unveiled details of its first 64-bit architecture, which it said would expand its reach into enterprise applications such as servers currently dominated by Intel.
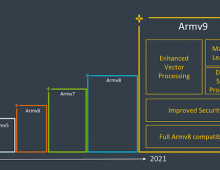
At ARM TechCon 2011 in Santa Clara, California, the company today disclosed technical details of its new ARMv8 architecture, the first ARM architecture to include a 64-bit instruction set. ARMv8 broadens the ARM architecture to embrace 64-bit processing and extends virtual addressing, building on the heritage of the 32-bit ARMv7 architecture upon which market cores such as the Cortex-A9 and Cortex-A15 processors are built.
Building on the industry standard 32-bit ARM architecture, the new ARMv8 architecture will expand the reach of ARM processor-based solutions into consumer and enterprise applications where extended virtual addressing and 64-bit data processing are required.
The ARMv8 architecture consists of two main execution states, AArch64 and AArch32. The AArch64 execution state introduces a new instruction set, A64 for 64-bit processing. The AArch32 state supports the existing ARM instruction set. The key features of the current ARMv7 architecture, including TrustZone, virtualization and NEON advanced SIMD, are maintained or extended in the ARMv8 architecture.
"With our increasingly connected world, the market for 32-bit processing continues to expand and evolve creating new opportunities for 32-bit ARMv7 based processors in embedded, real-time and open application platforms." said Mike Muller, CTO, ARM. "We believe the ARMv8 architecture is ideally suited to enable the ARM partnership to continue to grow in 32-bit application spaces and bring diverse, innovative and energy-efficient solutions to 64-bit processing markets."
The ARM compiler and Fast Models with ARMv8 support have already been made available to key ARM's ecosystem partners. Initial support for a range of open source operating systems, applications and third-party tools is already in development.
"ARM is an important partner for Microsoft," said KD Hallman, general manager, Microsoft Corp. "The evolution of ARM to support a 64-bit architecture is a significant development for ARM and for the ARM ecosystem. We look forward to witnessing this technology's potential to enhance future ARM-based solutions."
"The combination of NVIDIA?s leadership in energy-efficient, high-performance processing and the new ARMv8 architecture will enable game-shifting breakthroughs in devices across the full range of computing - from smartphones through to supercomputers," said Dan Vivoli, senior vice president, NVIDIA.
The ARMv8 architecture will enable the development of ARM architecture compatible devices that can be designed to maximize the benefits across both 32-bit and 64-bit application areas. This will bring the advantages of energy-efficient 64-bit computing to new applications such as high-end servers and computing, as well as offering backwards compatibility and migration for existing software through a consistent architecture.
The ARMv8 architecture specifications describing all aspects of the ARMv8 architecture are available now to ARM's partners under license. ARM will disclose processors based on ARMv8 during 2012, with consumer and enterprise prototype systems expected in 2014.
TSMC Production roadmap
TSMC representatives also talked about the collaboration of ARM with TSMC, through the "Open Innovation Platform" (OIP) and presented the latest TSMC Logic Technology roadmap. This includes both "High Performance", high-power and low-power, "Mobile computing" chips.
The company's current 28nm full node technology is offered with the option of both high-k metal gate (HKMG) and silicon oxynitride (SiON) material to support different applications and performance requirements.
Production of 28nm "CLN28HPM" chips are based on HKMG transistors and will be ready for production in the end of 2011.

TSMC's 20nm "High Performance" process includes the CLN20G (HKMG) scheduled for late 2012, and the CLN20 SoC (KKMG) for mobile computing, which will start mass production in early 2013. ARM's next generation application processor cores "Cortex-A15 (codename: Eagle)" and "Cortex-A7 (codename: Kingfisher)" are expected to be based on these processes. Compared to the 28nm generation, the 20nm process offers a 1.96x higher density for the logic gates as well a 1.2x faster operating speed.
The 14nm process is following the 20nm generation. According to TSMC's roadmap, test production of these 14nm chips (CLN14 FinFET) will begin in the first half of 2014, with production scheduled to start by the end of 2014.
Building on the industry standard 32-bit ARM architecture, the new ARMv8 architecture will expand the reach of ARM processor-based solutions into consumer and enterprise applications where extended virtual addressing and 64-bit data processing are required.
The ARMv8 architecture consists of two main execution states, AArch64 and AArch32. The AArch64 execution state introduces a new instruction set, A64 for 64-bit processing. The AArch32 state supports the existing ARM instruction set. The key features of the current ARMv7 architecture, including TrustZone, virtualization and NEON advanced SIMD, are maintained or extended in the ARMv8 architecture.
"With our increasingly connected world, the market for 32-bit processing continues to expand and evolve creating new opportunities for 32-bit ARMv7 based processors in embedded, real-time and open application platforms." said Mike Muller, CTO, ARM. "We believe the ARMv8 architecture is ideally suited to enable the ARM partnership to continue to grow in 32-bit application spaces and bring diverse, innovative and energy-efficient solutions to 64-bit processing markets."
The ARM compiler and Fast Models with ARMv8 support have already been made available to key ARM's ecosystem partners. Initial support for a range of open source operating systems, applications and third-party tools is already in development.
"ARM is an important partner for Microsoft," said KD Hallman, general manager, Microsoft Corp. "The evolution of ARM to support a 64-bit architecture is a significant development for ARM and for the ARM ecosystem. We look forward to witnessing this technology's potential to enhance future ARM-based solutions."
"The combination of NVIDIA?s leadership in energy-efficient, high-performance processing and the new ARMv8 architecture will enable game-shifting breakthroughs in devices across the full range of computing - from smartphones through to supercomputers," said Dan Vivoli, senior vice president, NVIDIA.
The ARMv8 architecture will enable the development of ARM architecture compatible devices that can be designed to maximize the benefits across both 32-bit and 64-bit application areas. This will bring the advantages of energy-efficient 64-bit computing to new applications such as high-end servers and computing, as well as offering backwards compatibility and migration for existing software through a consistent architecture.
The ARMv8 architecture specifications describing all aspects of the ARMv8 architecture are available now to ARM's partners under license. ARM will disclose processors based on ARMv8 during 2012, with consumer and enterprise prototype systems expected in 2014.
TSMC Production roadmap
TSMC representatives also talked about the collaboration of ARM with TSMC, through the "Open Innovation Platform" (OIP) and presented the latest TSMC Logic Technology roadmap. This includes both "High Performance", high-power and low-power, "Mobile computing" chips.
The company's current 28nm full node technology is offered with the option of both high-k metal gate (HKMG) and silicon oxynitride (SiON) material to support different applications and performance requirements.
Production of 28nm "CLN28HPM" chips are based on HKMG transistors and will be ready for production in the end of 2011.

TSMC's 20nm "High Performance" process includes the CLN20G (HKMG) scheduled for late 2012, and the CLN20 SoC (KKMG) for mobile computing, which will start mass production in early 2013. ARM's next generation application processor cores "Cortex-A15 (codename: Eagle)" and "Cortex-A7 (codename: Kingfisher)" are expected to be based on these processes. Compared to the 28nm generation, the 20nm process offers a 1.96x higher density for the logic gates as well a 1.2x faster operating speed.
The 14nm process is following the 20nm generation. According to TSMC's roadmap, test production of these 14nm chips (CLN14 FinFET) will begin in the first half of 2014, with production scheduled to start by the end of 2014.