
Hitachi Combines SSD Tier And SSD Cache Methods in Tiered Storage Systems
Hitachi has evaluated the methods currently followed to utilize SSD on the storage having both SSDs and HDDs, and proposed a new one that increases the storage I/O performance.
The amount of access workload to information systems has been
increasing. In general, input and output (I/O) activities have
a locality, and the number of I/Os for each area is different.
Typically, frequently accessed areas are stored on high
performance but still expensive SSDs (Solid State Drives), and
rarely accessed areas are stored on low performance and more
affordable HDDs (Hard Disk Drives). The result is a increased
I/O performance and a reduced system cost.
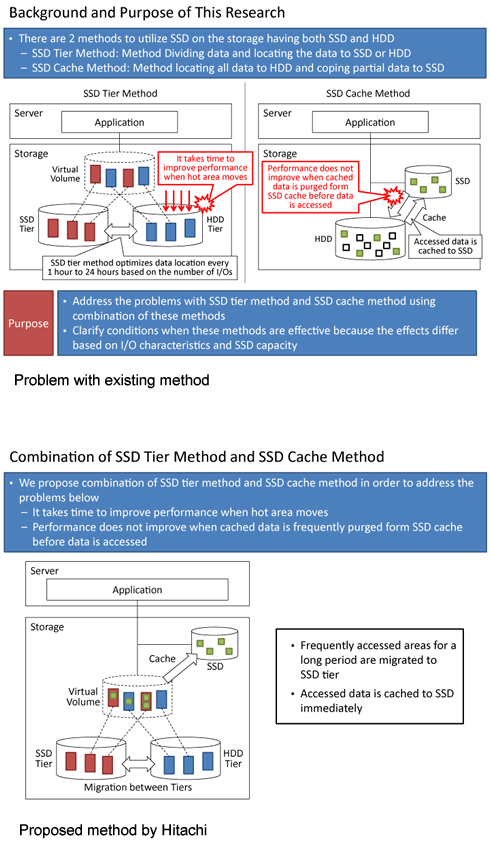
There are two methods to utilize SSD on the storage having both SSD and HDD.
- SSD Tier Method: Method Dividing data and locating the data to SSD or HDD
- SSD Cache Method: Method locating all data to HDD and coping partial data to SSD
The SSD tier method improves I/O performance by allocating hot areas to the SSD. However, it takes 1 hour to 24 hours to improve the I/O performance because this method optimizes data location every 1 hour to 24 hours when the hot areas move. Since the SSD cache method caches accessed area to SSD immediately, it improves the second and subsequence accesses to the area. Performance does not improve when cached data is frequently purged form SSD cache before data is accessed.
During the Second Asian Conference on Information Systems (ACIS 2013) held earlier this month in Phuket, Thailand, Yokohama Research Laboratory (YRL), Hitachi Ltd. presented a paper titled "Evaluation of SSD Tier Method and SSD Cache Method in Tiered Storage System."
Hitachi's researchers considered that by utilizing both methods simultaneously addresses the problems mentioned above. Assuming that the appropriate number of SSDs for tier and appropriate number of SSDs for cache may differ on the basis of the number of I/O, read-write ratio, and I/O locality, the researchers evaluated the effects of these methods by I/O simulation and clarified the conditions under these methods are effective.
The simulation result showed that the SSD tier method improves the storage I/O performance in write-intensive and low I/O locality workload with small SSD capacity. The SSD cache method is effective in read-intensive and high I/O locality workload with large SSD capacity. Hitachi claims that utilizing both methods simultaneously with write-intensive workload is the most effective.
"The storage I/O response time is reduced by up to 28% utilizing both methods simultaneously compared to using the SSD tier method or the SSD cache method separately," the researchers said.
There are two methods to utilize SSD on the storage having both SSD and HDD.
- SSD Tier Method: Method Dividing data and locating the data to SSD or HDD
- SSD Cache Method: Method locating all data to HDD and coping partial data to SSD
The SSD tier method improves I/O performance by allocating hot areas to the SSD. However, it takes 1 hour to 24 hours to improve the I/O performance because this method optimizes data location every 1 hour to 24 hours when the hot areas move. Since the SSD cache method caches accessed area to SSD immediately, it improves the second and subsequence accesses to the area. Performance does not improve when cached data is frequently purged form SSD cache before data is accessed.
During the Second Asian Conference on Information Systems (ACIS 2013) held earlier this month in Phuket, Thailand, Yokohama Research Laboratory (YRL), Hitachi Ltd. presented a paper titled "Evaluation of SSD Tier Method and SSD Cache Method in Tiered Storage System."
Hitachi's researchers considered that by utilizing both methods simultaneously addresses the problems mentioned above. Assuming that the appropriate number of SSDs for tier and appropriate number of SSDs for cache may differ on the basis of the number of I/O, read-write ratio, and I/O locality, the researchers evaluated the effects of these methods by I/O simulation and clarified the conditions under these methods are effective.

The simulation result showed that the SSD tier method improves the storage I/O performance in write-intensive and low I/O locality workload with small SSD capacity. The SSD cache method is effective in read-intensive and high I/O locality workload with large SSD capacity. Hitachi claims that utilizing both methods simultaneously with write-intensive workload is the most effective.
"The storage I/O response time is reduced by up to 28% utilizing both methods simultaneously compared to using the SSD tier method or the SSD cache method separately," the researchers said.





















