
Qualcomm Details New Snapdragon S4 SoCs
Qualcomm plans to introduce in 1H 2012 the 28nm Snapdragon S4 class of processors, which promise to offer always-on, high-speed internet coupled with highly capable electronics designed to deliver mobile users information and entertainment features.
The Snapdragon S4 processors are among the first mobile processors to be manufactured using the latest 28nm process technology that
provides advantages in frequency scaling, power consumption and size reduction.
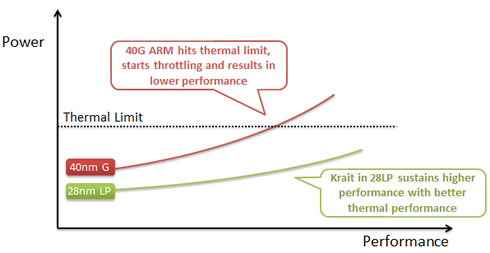
Texas instruments are also promising to release their 28nm TI's OMAP 5 processor in the second half of 2012. All the other chips schedulled for release at the same period such as Apple's A5, NVIDIA Tegra 3/Kal-El and Samsung Exynos 4212 are based on the 45nm/32nm processes.
Qualcomm has an ARM architecture license enabling it to build its own custom micro architectures that implement the ARM instruction set.
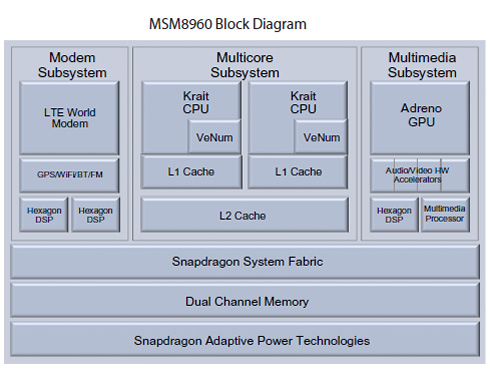
The Snapdragon S4 SoC will integrate LTE world mode/multimode modem, multicore CPUs with a frequency range of 1.5Ghz to 2.5Ghz per core (2 x Krait @ 1.5GHz) and supporting asynchronous symmetric multiprocessing (aSMP) for optimal balance of performance and power efficiency. Specifically, the Qualcomm MSM8960 Soc will use 2 x "Krait." @ 1.5GHz CPU cores. Connectivity options include integrated GPS, Bluetooth, WiFi, and FM.
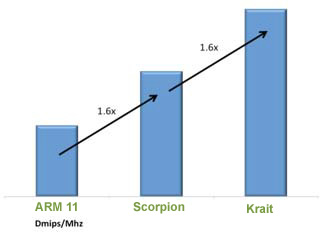
The Snapdragon S4 processors introduce Qualcomm?s second generation CPU, code-named "Krait." A new pipeline architecture increases the performance of Krait by over 60% compared to Qualcomm?s existing Scorpion CPU micro-architecture.
Krait also includes a performance enhanced floating-point and SIMD functional unit which maintains the 128-bit data-path. Optimized computational units, including those for double-precision calculations, speed through math intensive applications with minimal power consumption.
Krait also includes dual-channel memory. Dual-channel memory is critical in order for the processor to handle the large bandwidth requirements in multicore systems.
To achieve better power, performance and thermal envelope, Qualcomm designed the Krait micro-architecture as an asynchronous Symmetrical Multi-Processor system or aSMP. The difference between an aSMP and a synchronous SMP system is:
- Independent clock and voltage: Each core in the aSMP system has a dedicated voltage and clock including the L2 cache. This enables each CPU core to run at the most efficient power point or voltage and frequency depending on the type of workload being executed.
- 25?40% power improvement: The aSMP architecture results in a 25?40% power improvement over current synchronous SMP architectures.
- Standby power: In aSMP, each core that is not being used can be completely collapsed independently resulting in no power consumption in idle state. - Reduced complexity: aSMP also eliminates the need for "companion" or "little" cores since each core in an aSMP system can be operated in low power mode due to the independent voltage and frequency control per core thus reducing the need for hypervisors or more complex software management of disparate cores.
The S4 processor family incorporates the latest in GPU technology starting with the Adreno 225 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
According to Qualcomm, the Adreno 225 GPU delivers 50% greater graphics processing power over the previous generation Adreno GPU, Adreno 220, and six times the processing power of Adreno 200.
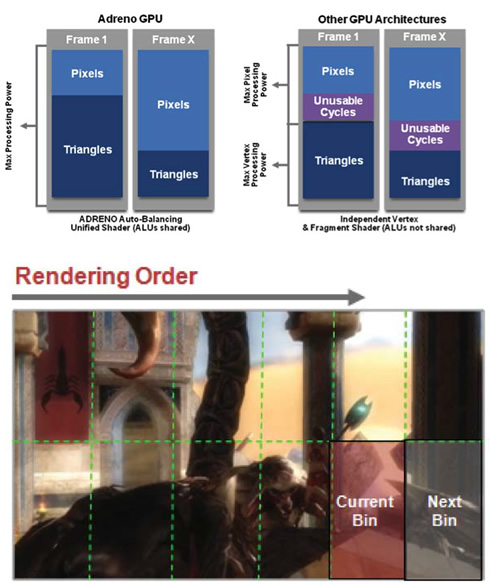
Built on a proven track record of highly capable Adreno embedded processors, the Adreno 225 GPU is a fully programmable OpenGL ES 2.0 GPU with a Unified Shader Architecture (USA). Adreno?s USA maximizes the processing power of the GPU by off ering flexible vertex and shader processing. This architecture is a significant leap forward in visual graphics quality from earlier "fixed function" OpenGL-Es 1.x GPUs.
The Adreno 225 GPU has twice the memory bandwidth of its predecessor, which further contributes to better graphics performance at higher display resolutions. The APIs supported by Adreno 225 include OpenGL ES 1.1, OpenGL ES 2.0 and DX9.3.
Adreno 225 also includes more features, primarily to support DirectX 9.3 for Windows 8.
Qualcomm MSM8960 is on-track for a release sometime in the first half of next year. Assuming Qualcomm can deliver on its claims, performance alone would be enough to make this chip succesful. Improved power characteristics and integrated LTE baseband really complete the package though.

Texas instruments are also promising to release their 28nm TI's OMAP 5 processor in the second half of 2012. All the other chips schedulled for release at the same period such as Apple's A5, NVIDIA Tegra 3/Kal-El and Samsung Exynos 4212 are based on the 45nm/32nm processes.
Qualcomm has an ARM architecture license enabling it to build its own custom micro architectures that implement the ARM instruction set.

The Snapdragon S4 SoC will integrate LTE world mode/multimode modem, multicore CPUs with a frequency range of 1.5Ghz to 2.5Ghz per core (2 x Krait @ 1.5GHz) and supporting asynchronous symmetric multiprocessing (aSMP) for optimal balance of performance and power efficiency. Specifically, the Qualcomm MSM8960 Soc will use 2 x "Krait." @ 1.5GHz CPU cores. Connectivity options include integrated GPS, Bluetooth, WiFi, and FM.
The Snapdragon S4 processors introduce Qualcomm?s second generation CPU, code-named "Krait." A new pipeline architecture increases the performance of Krait by over 60% compared to Qualcomm?s existing Scorpion CPU micro-architecture.

Krait also includes a performance enhanced floating-point and SIMD functional unit which maintains the 128-bit data-path. Optimized computational units, including those for double-precision calculations, speed through math intensive applications with minimal power consumption.
Krait also includes dual-channel memory. Dual-channel memory is critical in order for the processor to handle the large bandwidth requirements in multicore systems.
To achieve better power, performance and thermal envelope, Qualcomm designed the Krait micro-architecture as an asynchronous Symmetrical Multi-Processor system or aSMP. The difference between an aSMP and a synchronous SMP system is:
- Independent clock and voltage: Each core in the aSMP system has a dedicated voltage and clock including the L2 cache. This enables each CPU core to run at the most efficient power point or voltage and frequency depending on the type of workload being executed.
- 25?40% power improvement: The aSMP architecture results in a 25?40% power improvement over current synchronous SMP architectures.
- Standby power: In aSMP, each core that is not being used can be completely collapsed independently resulting in no power consumption in idle state. - Reduced complexity: aSMP also eliminates the need for "companion" or "little" cores since each core in an aSMP system can be operated in low power mode due to the independent voltage and frequency control per core thus reducing the need for hypervisors or more complex software management of disparate cores.
The S4 processor family incorporates the latest in GPU technology starting with the Adreno 225 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
According to Qualcomm, the Adreno 225 GPU delivers 50% greater graphics processing power over the previous generation Adreno GPU, Adreno 220, and six times the processing power of Adreno 200.

Built on a proven track record of highly capable Adreno embedded processors, the Adreno 225 GPU is a fully programmable OpenGL ES 2.0 GPU with a Unified Shader Architecture (USA). Adreno?s USA maximizes the processing power of the GPU by off ering flexible vertex and shader processing. This architecture is a significant leap forward in visual graphics quality from earlier "fixed function" OpenGL-Es 1.x GPUs.
The Adreno 225 GPU has twice the memory bandwidth of its predecessor, which further contributes to better graphics performance at higher display resolutions. The APIs supported by Adreno 225 include OpenGL ES 1.1, OpenGL ES 2.0 and DX9.3.
Adreno 225 also includes more features, primarily to support DirectX 9.3 for Windows 8.
Qualcomm MSM8960 is on-track for a release sometime in the first half of next year. Assuming Qualcomm can deliver on its claims, performance alone would be enough to make this chip succesful. Improved power characteristics and integrated LTE baseband really complete the package though.





















