
Qualcomm Zeroth Processors Aim At Brain-Inspired Computing
Qualcomm's Research and Development teams have been working on a new computer processor that mimics the human brain and nervous system so devices can have embedded cognition driven by brain inspired computing, in what the company calls Qualcomm Zeroth processing.
The researchers want Qualcomm Zeroth products to not only mimic human-like perception but also have the ability to learn how biological brains do. Instead of preprogramming behaviors and outcomes with a lot of code, they have developed a suite of software tools that enable devices to learn as they go and get feedback from their environment.
In this video, the researchers outfitted a robot with a Qualcomm Zeroth processor and placed it in an environment with colored boxes. They then able to teach it to visit white boxes only. They did this through dopaminergic-based learning, a.k.a. positive reinforcement?not by programming lines of code.
Another major pillar of Zeroth processor function is striving to replicate the efficiency with which our senses and our brain communicate information. Neuroscientists have created mathematical models that accurately characterize biological neuron behavior when they are sending, receiving or processing information. Neurons send precisely timed electrical pulses referred to as "spikes" only when a certain voltage threshold in a biological cell?s membrane is reached. These spiking neural networks (SNN) encode and transmit data very efficiently in both how our senses gather information from the environment and then how our brain processes and fuses all of it together.
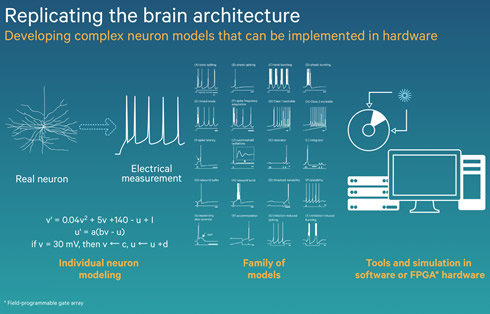
The final goal of Qualcomm Zeroth is to create, define and standardize this new processing architecture - Qualcomm calls it a Neural Processing Unit (NPU.) The company envisions NPU's in a variety of different devices, but also able to live side-by-side in future system-on-chips. This way you can develop programs using traditional programing languages, or tap into the NPU to train the device for human-like interaction and behavior.

In this video, the researchers outfitted a robot with a Qualcomm Zeroth processor and placed it in an environment with colored boxes. They then able to teach it to visit white boxes only. They did this through dopaminergic-based learning, a.k.a. positive reinforcement?not by programming lines of code.
Another major pillar of Zeroth processor function is striving to replicate the efficiency with which our senses and our brain communicate information. Neuroscientists have created mathematical models that accurately characterize biological neuron behavior when they are sending, receiving or processing information. Neurons send precisely timed electrical pulses referred to as "spikes" only when a certain voltage threshold in a biological cell?s membrane is reached. These spiking neural networks (SNN) encode and transmit data very efficiently in both how our senses gather information from the environment and then how our brain processes and fuses all of it together.

The final goal of Qualcomm Zeroth is to create, define and standardize this new processing architecture - Qualcomm calls it a Neural Processing Unit (NPU.) The company envisions NPU's in a variety of different devices, but also able to live side-by-side in future system-on-chips. This way you can develop programs using traditional programing languages, or tap into the NPU to train the device for human-like interaction and behavior.






















