Summary of Intel's Latest Product Roadmap
During the recent Architecture Day 2020, Intel executives showcased new architectures and innovations for what the company calls "the Intelligent Era."
"We believe the next era will be the intelligent era. An era where we will experience 100 billion intelligent connected devices. Exascale performance and architecture will make this intelligence available to all, enriching our lives in more ways than we can imagine today. This is a future that inspires and motivates me and my fellow Intel architects every day," said Raja Koduri, Chief Architect, General Manager, Intel Architecture, Graphics, and Software.
At the virtual event, Intel announced progress with its mix of scalar, vector, matrix and spatial architectures – designed with an updated process technology - although still based on the 10nm - , fed by disruptive memory hierarchies, integrated into systems with advanced packaging, deployed at hyperscale with lightspeed interconnect links, unified by a single software abstraction, and developed with benchmark defining security features.
Intel provided more details about its disaggregated design methodology and the company's packaging roadmap. The chip maker also demonstrated its mastering of fine bump pitches in EMIB and Foveros technologies through several product iterations in graphics and FPGAs, and on the client with Lakefield.
Intel also announced advancements in its transistor roadmap by introducing a new 10nm SuperFin technology, a redefinition of the FinFET with new SuperMIM capacitors that enables the largest single, intranode enhancement in Intel’s history, promising to deliver performance improvements comparable to a full-node transition.
Intel integrates its next-generation Willow Cove CPU architecture with its 10nm SuperFin technology in the new Tiger Lake SoC architecture for mobile client. The upcoming Tiger Lake system-on-chip architecture promises to provide a generational leap in CPU performance, leadership graphics, leadership artificial intelligence (AI), more memory bandwidth, additional security features, better display, better video and more.
10nm SuperFin technology combines Intel’s FinFET transistors with Super metal insulator metalcapacitor.

Intel said that the SuperFin technology offers enhanced epitaxial source/drain, improved gate process and additional gate pitch to enable greater performance by:
- Enhancing epitaxial growth of crystal structures on the source and drain, thus increasing strain and reducing resistance to allow more current through the channel.oImproving gate process to drive higher channel mobility, which enables charge carriers to move more quickly.
- Providing an additional gate pitch option for higher drive current in certain chip functions that require the utmost performance.
- Using a novel thin barrier to reduceresistance by 30% and enhance interconnect performance.
- Delivering a 5x increase in capacitance within the same footprint when compared to industry standard, driving a voltage droop reduction that translates to improved product performance.
The technology is enabled by a new class of “Hi-K” dielectric materials stacked in ultra-thin layers just several angstroms thick to form a repeating “super lattice” structure. This is an industry-first technology that is ahead of current capabilities of other manufacturers.
Intel’s next-generation mobile processor, code-named Tiger Lake, is based on 10nm SuperFin technology. Tiger Lake is in production, and shipping to customers with original equipment manufacturer systems is expected for the holiday season.

Willow Cove and Tiger Lake CPU Architectures
Willow Cove is Intel’s next-generation CPU microarchitecture. Built on the latest process advancements, 10nm SuperFin technology and the foundation of the Sunny Cove architecture, Willow Cove delivers more than a generational increase in CPU performance with large frequency improvements and increased power efficiency. It also introduces a redesigned caching architecture to a larger non-inclusive 1.25MBMLC and security enhancements with Intel Control Flow Enforcement Technology.
Tiger Lake will offer intelligent performance and advancements in the key vectors of compute. With optimizations spanning the CPU, AI accelerators and being the first system-on-chip architecture with the newXe-LP graphics microarchitecture, Tiger Lake promises to deliver more than a generational increase in CPU performance, massive AI performance improvements and a huge leap in graphics performance with a full set of best-in-class IPs throughout the SoC like the new, integrated Thunderbolt.
Tiger Lake SoC architecture offers:
- New Willow Cove CPU core with significant frequency uplift leveraging 10nm SuperFin technology advancements.
- New Xe graphics with up to 96 execution units (EUs ) with significant performance-per-watt efficiency improvements.
- Power management –autonomous dynamic voltage frequency scaling in coherent fabric, increased fully integrated voltage regulator efficiency.
- Fabrics and memory –2x increase in coherent fabric bandwidth, ~86GB/s memory bandwidth, validated LP4x-4267, DDR4-3200; LP5-5400 architecture capability.
- Gaussian Network Accelerator (GNA)2.0 dedicated IP for low-power neural inferencing offloading from the CPU. ~20% lower CPUutilizationon GNA vs. CPU (running noise suppression workload).
- IO -Integrated TB4/USB4, integrated PCIe Gen 4 on CPU for low-latency, high-bandwidth device access to memory.
- Display –up to 64GB/s of isochronous bandwidth to memory for multiple high-resolution displays. Dedicated fabric path to memory to maintain quality of service.
- IPU6 –up to six sensors with 4K30 video, 27MP image,up to 4K90 and 42MP image architectural capability.
In addition to Tiger Lake, Intel provided a deep dive into its next generation Intel Agilex FPGA, which promises to provide breakthrough performance per watt. In fact, Intel showcased two generations of disaggregated products using EMIB and shared the first results of its 224 Gbps transceivers.

Packaging

Intel said that its Hybrid bonding test chip taped out in Q2, 2020. Hybrid bonding is an alternative to the traditional “thermocompression” bonding used in most of today’s packaging technologies. This new technology enables very aggressive bump pitches of 10 microns and below, delivering much higher interconnect density and bandwidth, along with lower power.
Hybrid Architecture
Intel is advancing its hybrid architecture with Alder Lake, the company’s next-generation client product. Alder Lake will combine two upcoming architectures: Golden Cove and Gracemont, optimized to offer great performanceper watt.
Data Center Architectures

On the data center front, Intel announced that its first Xe-HP chip is sampling to customers. Xe-HP is the industry’s first multitiled, highly scalable, high-performance GPU architecture,providing petaflop-scale AI performance and rack-level media performance in a single package based on our EMIB technology. Xe-HP will leverage enhanced SuperFin technology.
- Ice Lake,the first 10nm-based Intel Xeon calable processortargetedfor the end of 2020, will deliver significant performance in both throughput and responsiveness across workloads. It will bring a set of technologies,including total memory encryption, PCIe Gen 4and eight memory channels with instruction-set architecture to speed up cryptoprocessing. Variants for network storage and internet of things will also be introduced as part of the Ice Lake family.
- Sapphire Rapids is Intel’s next-generation Xeon Scalable processor based on enhanced SuperFin technologyand will offer leading industry-standard technologies including DDR5, PCIe Gen 5and Compute Express Link 1.1. Sapphire Rapids will be the CPU used in the Aurora Exascale supercomputer system at Argonne National Lab. It will continue our strategy of built-in AI acceleration witha new accelerator called Advanced Matrix Extensions. Sapphire Rapids is expected to start initial production shipments in the second half of 2021.
XeGraphics Architectures

Intel also highlighted how Intel’s Xe GPU architecture is the foundation that helps the company build GPUs that are scalable from teraflops to petaflops.
Xe-LP powers leadership graphics in Tiger Lake and is Intel's most efficient microarchitecture for PC and mobile computing platforms. Xe-LP also powers Intel's first discrete GPU in more than 20 years, codenamed DG1. This GPU is now in production.
Intel also introduced the first Intel server GPU, powered by Xe-LP. This GPU will ship later this year with the promise to deliver class-leading stream density and visual quality for media transcode and streaming.
Intel detailed the Xe-LP (low power) microarchitecture and software optimized to deliver efficient performance for mobile platforms. Xe-LP is Intel’s most efficient architecture for PC and mobile computing platforms with up to 96 EUs, and comes with new architecture designs including asynchronous compute, view instancing, sampler feedback, updated media engine with AV1 and updated display engine. This will enable new end-user features with instant game tuning, capture, and stream-and-image sharpening. On software optimization, Xe-LP will have driver improvements with a new DX11 path and optimized compiler.
The firstXe-HP chip has been powered on and back from the labs. Xe-HP is the industry’s first multi-tiled, highly scalable, high performance architecture, providing data center-class, rack-level media performance, GPU scalability and AI optimization. It covers a dynamic range of compute from one tile, to two and four tiles, functioning like a multicore GPU.
At Architecture Day, Intel demonstrated Xe-HP transcoding 10 full streams of high-quality 4K video at 60 frames per secondon a single tile. Another demo showed the compute scalability of Xe-HP across multiple tiles. Intel is now sampling Xe-HP with key customers and plansto enable it in Intel DevCloud for developers. Xe-HP will be available next year.
Intel introduced a new Xe microarchitecture variant, Xe-HPG, a gaming-optimized microarchitecture, combining good performance-per-watt building blocks from Xe-LP, leveraging the scale from Xe-HP for a bigger configuration and compute frequency optimization from Xe-HPC. A new memory subsystem based on GDDR6 is added to improve performanceper dollar and Xe-HPG will have accelerated ray tracing support. Xe-HPG is expected to start shippingin 2021.
The Intel Server GPU (SG1) is Intel’s first discrete GPU based on Xe architecture for the data center. SG1 brings performance from four DG1s in a small form factor to the data center and is targeted for low-latency, high-density Android cloud gaming and video streaming. SG1 will ship later this year and will be in production soon.
Intel’s first Xe-based discrete GPU, code-named DG1, is in production and on track to start shipping in 2020. DG1 is now available within the Intel DevCloud, accessible to early access users. Announced at CES, itis Intel’s first discrete GPU for PCs based on Xe-LP microarchitecture.
New features were also introduced to the Intel Graphics Command Center, including instant game tuning andgame sharpening.
- Instant game tuning is a game-specific driver. Fixes and optimizations can be pushed to users faster than before and without a full driver download and install. It will only require a single opt-in from the user per game.
- Game sharpening uses perceptual adaptive sharpening –a compute shader-based adaptive sharpening algorithm that boosts image clarity in games. This feature is particularly useful for titles that use resolution scaling to balance performance and imagequality and is an opt-in feature within IGCC.
On the software front, Intel's vision is to provide developers a unified, standards-based programming model across all its XPU architectures. The company is executing on that vision with its oneAPI Gold release available later this year. Intel also announced that it is offering DG1 early access to developers in Intel DevCloud, enabling them start developing with oneAPI without need for any setups, downloads and hardware installs.
On the memory front, as part of the 3rd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processor launch (code-named “Cooper Lake”), Intel announced its 2nd Gen Intel Optan persistent memory product (code-named “Barlow Pass”). The company said it remained on track to move Intel’s 4-bit-per-cell QLC into production by the end of 2020.

Intel also took a deeper look at how its is advancing security amid a constantly evolving threat landscape. This includes the introduction of new technologies, such Intel Control-Flow Enforcement Technology, which delivers CPU-level security structures to help protect against common malware attack methods. And, Intel gave the first look at our longer-term vision around foundational security, workload protection and software reliability.
Intel has made progress in advancing interconnect, too. The company announced in March 2019 that it was working with the industry for broad support for Compute Express Link, designed to accelerate next-generation data center performance and to be offered in Sapphire Rapids. Intel has also had a lead with silicon photonics in terms of customer engagements, and as the data center continues its transformation, Intel is addressing their needs through leadership speeds and foundational and SmartNIC products for network processing offloads.
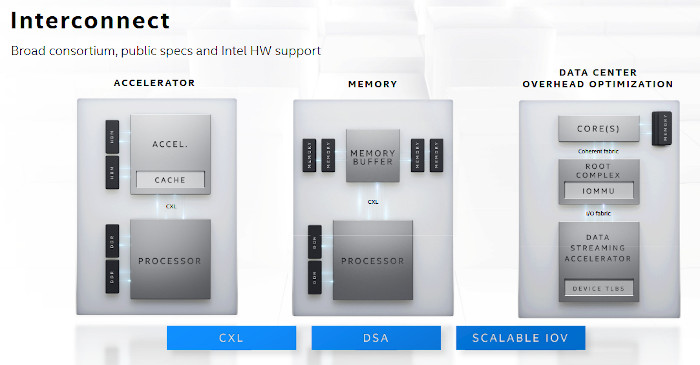
Intel fellows and architects are working on technology for 2021, 2022 and beyond. Intel provided a glimpse into its product vision for client and data center leveraging for all six pillars and disaggregated design.
The head of Intel Labs also provided a look at where emerging research areas can get us 100x to 1000x improvements in compute efficiency, including a sneak peek at neuromorphic architectures being researched in Intel's labs.