
Qualcomm Launches New 7nm Snapdragon X55 5G Chip For Smartphones
Qualcomm on Tuesday introduced its second-generation modem chips to connect phones to 5G networks, speeding up the race around faster wireless data connections expected to begin rolling out later this year.
The Snapdragon X55 5G New Radio (NR) modem is a 7-nanometer single-chip integrated 5G to 2G multimode modem that supports 5G NR mmWave and sub-6 GHz spectrum bands with up to 7 gigabits per second (Gbps) download speeds and 3 Gbps upload speeds over 5G, and Category 22 LTE with up to 2.5 Gbps LTE download speeds. The modem is designed for global 5G rollouts with support for all major frequency bands, whether mmWave or sub-6 GHz, supports TDD and FDD modes of operations and is capable of both Standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) network deployments. In addition to deployments in greenfield frequency bands allocated for 5G, the Snapdragon X55 modem is engineered to support dynamic spectrum sharing between 4G and 5G, enabling operators to accelerate 5G deployments by using their existing 4G spectrum holdings to deliver both 4G & 5G services dynamically.
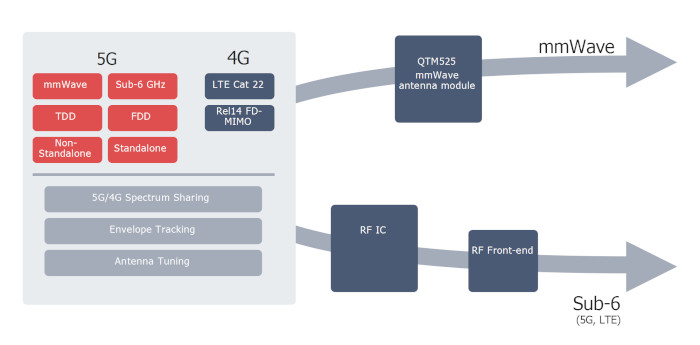
The Snapdragon X55 5G modem pairs with Qualcomm's newly announced 5G mmWave antenna module (QTM525), a new single-chip 14nm RF transceiver for 5G sub-6 GHz and LTE, and sub-6 GHz RF front-end modules to deliver the next generation modem-to-antenna solution for all major spectrum bands.
The Snapdragon X55 is the first announced modem to support 100 MHz envelope tracking technology, and adaptive antenna tuning for 5G sub-6 GHz, designed for power-efficient connectivity for the next generation of smartphones and mobile devices.
The chip is urrently sampling to Qualcomm's customers and expected to be in commercial devices by late 2019.
Specifications Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 Modem- 5G Technology: 5G NR
- 5G Spectrum: mmWave, sub-6 GHz, 5G/4G spectrum sharing
- 5G Modes: FDD, TDD, SA (standalone), NSA (non-standalone)
- 5G mmWave specs: 800 MHz bandwidth, 8 carriers, 2x2 MIMO
- 5G sub-6 GHz specs: 100 MHz bandwidth, 4x4 MIMO
- 5G Peak Download Speed: 7 Gbps
- 5G Peak Upload Speed: 3 Gbps
- 5G RF: 100 MHz envelope tracking, Adaptive antenna tuning
LTE Downlink Features
- Downlink Carrier Aggregation: 7x20 MHz carrier aggregation
- Downlink LTE MIMO: 4x4 MIMO
- Downlink LTE Streams: 24 LTE streams
- Downlink QAM: Up to 1024-QAM
LTE Uplink Features
- Uplink Technology: Uplink Data Compression (UDC)
- Uplink Carrier Aggregation: 3x20 MHz carrier aggregation
LTE Speed
- LTE Peak Download Speed: 2.5 Gbps
- LTE Peak Upload Speed: 316 Mbps
Cellular Technology: WCDMA (DB-DC-HSDPA, DC-HSUPA), TD-SCDMA, CDMA 1x, EV-DO, GSM/EDGE
LTE Technology: LTE FDD, LTE TDD including CBRS support, LAA, LTE Broadcast
5G Technology: 5G NR FDD, 5G NR TDD, SA, NSA
RFFE: 5G adaptive antenna tuning, 5G envelope tracking
Qualcomm is hoping the device will fuel the spread of 5G phones. While Chinese phone makers such as Xiaomi last year used Qualcomm’s first-generation chip for small batches of 5G phones, the second-generation chip announced Tuesday is aimed at mass production.
The move comes a day before Samsung is set to announce its new flagship Galaxy series phones. Samsung and Qualcomm in December publicly committed to working together to release a 5G phone this year, and analysts believe Samsung will unveil a 5G version of its flagship models this week.
Huawei Technologies Co Ltd, the world’s third-largest smart phone maker, last month announced that it has built a 5G chip that it will use in its own phones. Samsung, too, has a 5G modem called the Exynos 5100 that will power many Samsung devices sold outside the United States. MediaTek Inc also has 5G chip, with Intel targeting the second half of this year for a release.
Carriers in Korea and China, meantime, are set to start turning on the networks this spring, with carriers in the United States planning rollouts for later this year.
Apple has not said when the iPhone will have 5G capabilities. In its iPhones released last year, Apple dropped Qualcomm’s chips in favor of those from Intel. Apple disclosed in a court hearing last month that it had held talks with MediaTek and Samsung about supplying modems for 2019 iPhones, but Bloomberg earlier reported that 5G iPhones will not appear until 2020.
Qualcomm is also introducing several chips surrounding the modem. Some elements of 5G phones, such as the design of antennas and chips for handling analog radio waves, are more complicated than previous generations of phones. Qualcomm aims to speed up adoption of 5G by also selling those technologies to phone makers.
Second Generation 5G RF Front-End Solutions for 5G Multimode Mobile Devices
Qualcomm announced its second-generation RF front-end (RFFE) solutions for 5G multi-mode mobile devices. The new products represent an RF solution designed to work with the new Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 5G modem.
The RFFE solutions include the Qualcomm QTM525 5G mmWave antenna module, which builds on the innovation of Qualcomm Technologies’ first mmWave antenna module by reducing the height of the module to support 5G smartphone designs sleeker than 8 millimeters thick. The new module adds support for band n258 (24.25 – 27.5 GHz) for North America, Europe and Australia on top of bands n257 (26.5 – 29.5 GHz), n260 (37 – 40 GHz) and n261 (27.5 – 28.35 GHz) already supported by its predecessors.
Qualcomm is also launching the first announced 5G 100MHz envelope tracking solution, QET6100, as well as a family of integrated 5G/4G power amplifier (PA) and diversity modules, and the QAT3555 5G adaptive antenna tuning solution.
The QET6100 extends envelope tracking technology to the wide 100 MHz uplink bandwidth and 256-QAM modulation needed for 5G NR, previously considered unattainable. This can achieve up to double the power efficiency compared to the alternative average power tracking technology, enabling faster devices with long battery life, as well as improvements in network coverage and capacity – key considerations for network operators.
Qualcomm Technologies’ new RFFE PA and diversity modules include:
- PA modules which pair with QET6100 to support 100 MHz 5G envelope tracking. QPM6585, QPM5677 and QPM5679 for bands n41, n77/78 and n79 respectively.
- Mid/High-band 5G/4G PA module QPM5670 features integrated LNA, switch, filters and 5G hexaplexer.
- Low-band 5G/4G PA module QPM5621 with integrated LNA, switch and filters, and support for low-band/low-band carrier aggregation and dual connectivity.
- Diversity module family QDM58xx, featuring integrated 5G/4G LNA, switch and filters for receive diversity and MIMO support for sub-6 GHz bands.
Qualcomm expects to start sampling these products to customers in the first half of 2019.
5G NR Technology and new applications at Mobile World Congress 2019
Qualcomm will demonstrate advanced 5G New Radio (NR) technologies at Mobile World Congress Barcelona 2019 to showcase its roadmap and the broad range 5G technology and solutions being applied across new applications and use cases. The live demos will highlight Qualcomm Technologies’ use of enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) beyond smartphones based on 3GPP Release 15 (R15) and showcase new use cases that expand 5G NR to new industries in 3GPP Release 16 and beyond.
To demonstrate the opportunities for 5G eMBB based on 3GPP R15 and beyond, Qualcomm will show the benefits of deploying 5G NR millimeter wave (mmWave) for indoor use cases, two such examples being private enterprises and high-density venues. This system simulation complements the indoor mmWave OTA test network and highlights the user experiences achieved with indoor mmWave deployments, which are designed to bring high-capacity, multi-Gigabit and low-latency connectivity to smartphones, laptops, and other connected devices.
Qualcomm will shave a live 5G network at Mobile World Congress. The company will showcase boundless extended reality (XR) powered by the Qualcomm Snapdragon X50 5G modem, where on-device processing is augmented by additional edge cloud processing over a low-latency 5G link.
In addition, Qualcomm will showcase 5G NR sub-6 GHz evolution in R16. The company's sub-6 GHz advanced simulation demonstrates potential future improvements of 5G NR networks and devices, including enhanced massive MIMO operations and device power-saving features. The simulation also shows how 5G, when complemented with edge cloud processing, can enable new ultra-low latency services such as wide-area augmented reality.
As 3GPP R16 is expanding 5G NR into new industries, Qualcomm is pushing the technology boundary to optimize 5G for new use cases. Industrial IoT (IIoT) with new functionality for enhanced ultra-reliable low-latency communication (eURLLC) will bring flexibility to future factories with wireless connectivity controlling mission critical machines. This year’s IIoT demo will show 99.9999% reliability was achieved in the company’s over-the-air 5G test network.
Another 5G evolution demonstration on display is showcasing how 5G in shared and unlicensed spectrum (NR-U) can be utilized with coordinated multi-point (CoMP) in local private 5G networks to provide higher performance in terms of network capacity, user throughput and reliability. These benefits in shared/unlicensed spectrum are applicable in both single operator deployments as well as in multi-operator deployments, where spatial multiplexing allows multiple deployments to share the same spectrum band simultaneously.
Finally, building on 3GPP Release 14 C-V2X momentum, 3GPP Release 16 5G NR C-V2X is designed to not only be backward compatible with Release 14, but also help enable use cases beyond just safety by sharing information directly between vehicles and road side units. Qualcomm Technologies’ demo will illustrate that even during early 5G NR C-V2X deployments, the technology can enable lower energy usage and faster travel for autonomous vehicles, as well as higher situational awareness for assisting drivers and as we move to higher levels of autonomy.





















