
AMD Financial Analyst Day: Epyc, Ryzen Mobile and PRO, Threadripper and Radeon RX Vega
AMD held its AMD 2017 Financial Analyst Day presentation and provided a glimpse of the upcoming CPU and GPU products, including the Ryzen-based "EPYC" CPU for datacenters, Ryzen Mobile CPUs, multi-core Ryzen PROs for the desktop, the massive 16-core Threadripper desktop parts and the new Radeon Vega Frontier Edition.
Starting with the AMD "EPYC," it is the brand name for Data-center CPU based on Ryzen. Previously known as "Naples", the server processors will be based on based on the "RyZen" x86 processing engine with up to 32 cores and 64 simultaneous threads, eight memory channels, supporting up to 2TB RAM per CPU and 128 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Memory can run 2400/2677 MHz per channel. The memory controller is also capable of using bigger than 16GB DIMMs and in total you could fit 4 TB of DDR4 memory. "EPYC" will also feature a dedicated security engine.

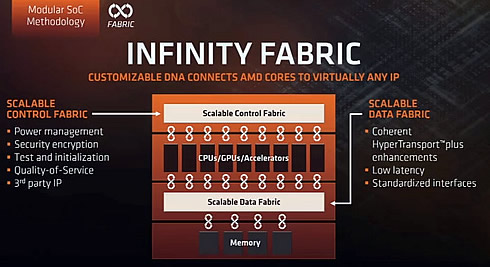
The "EPYC" SoC features a 128 high-speed I/O-lanesof PCI 3, negating the need for a separate chip-set. When you couple two processors in SMT, the IO is shared though and 64 lanes will be used for the interconnect in-between the two Naples processors . Each "EPYC" processor has four Zen based 8-core dies interconnected though what AMD calls "Infinity fabric".
Starting with new 2017 product introductions, future AMD products are also planned to harness the power of breakthrough AMD Infinity Fabric technology to efficiently create highly-scalable SoCs and platforms.
AMD claims that a single EPYC processor exceeds the performance of the competitive Intel E5-2650 v4 two-socket / two-processor platform in a head-to-head comparison. AMD says that a single-socket EPYC chip is 50% faster than Intel's chip, while delivering significantly lower power consumption and an up to 30% TCO advantage. The company also says that EPYC also exceeds today's top competitive offering on critical parameters, with 45% more cores, 60% more input/output capacity (I/O), and 122% more memory bandwidth.
The table below shows a side-by-side comparison of AMD Epyc and competitive Intel Xeon products. All the information in the table is for 1S configurations, although both Epyc and Xeon E5 are dual-socket capable. AMD's table shows that Epyc is not only pushing well beyond Xeon E3 limitations, but also exceeding Xeon E5 v4 integration and features.

With this example, AMD underlined that the Epyc architecture will enable uniquely capable 1S server solutions. The company says that economics, coupled with memory and I/O scaling, are sufficient justification for data center customers to adopt 1S designs in volume, as AMD's Epyc SoC addresses the majority of 1S architectural and economic objections.
In other words, AMD believes that buying overprovisioned 2S servers will be throwing money away once Epyc 1S servers are generally available.
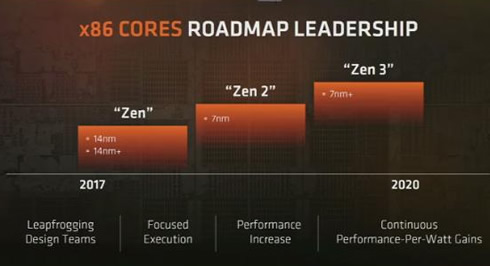
EPYC will be followed by the 7nm, Zen2-based "Rome" chips and the Zen3, 7nm+ "Milan" chips in 2010.
AMD also unveiled that it will bring to the market the first Ryzen Mobile Solutions by the end of this year. Ryzen Mobile APUs (codenamed "Raven Ridge") integrate a 4-core, 8-thread "Zen"-based CPU and high-performance "Vega" graphics. These will in two-in-1 systems, ultraportable, and gaming products. These Zen and Vega foundations should deliver 50% more CPU performance and 40% more GPU performance, help AMD achieve an up to 50% increase in power efficiency on their mobile platformcompared to their 7th Gen APU solutions.

AMD's x86 cores roadmap shows the release of Zen 2 sometime next year. It will be based on 7nm and will be followed by the 7nm Zen 3 in 2020.
AMD also announced Ryzen Pro, new Ryzen-based processors for the commercial market. They will be available in both desktop and mobiles.
Targeted for commercial, enterprise, and public sector implementation, Ryzen PRO processors are designed to deliver powerful multi-threaded performance for business PCs with workstation-class performance, silicon-level security, reliable solutions with enterprise-class support and top-to-bottom manageability.
Ryzen PRO desktop solutions are slated for availability in the second half of 2017. Ryzen PRO mobile is planned for first half of 2018.


"Threadripper" will be AMD's 16-core/32 thread, enthusiast-grade desktop part. It will be available Summer 2017 and more information will become available during Computex.
If previous Ryzen chip performance is a predictor of how Threadripper will do, the 32-thread chip should easily surpass Intel's current 10-core Core i7-6950X in heavily multi-threaded and heavy multi-tasking chores.
With Intel's rumored Core i9 expected to max out with 12 cores, AMD's 16-core Threadripper could very well steal its thunder.

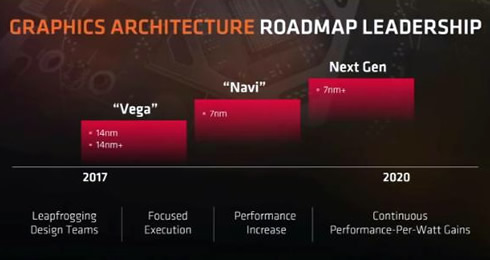
In the Radeon front, the Rx Vega will become available in June. The GPUs will based on 14nm and 14nm+ node processes. AMD underlined the benefits of the new Vega architecture and heterogeneous computing. AMD sais that Vega will play a significant role in the data center environments, and also compared it with the Nvidia P100 card in the DeepBench benchmark. As it was expected in a presentation, AMD's Vega scored 88 Ms, while the the NVIDIA setup 133 (lower is better.)
AMD's graphics architecture roadmap includes the next-gen 7nm "Navi" in 2018-2019, followed by a new unnamed for now architecture in 2020. The latter will be based on 7nm+ node.
AMD will also launch the Radeon Vega Frontier Edition graphics card this June. Described as the world's most advanced card, it has been designed for data scientists and product designers (machine learning and advanced visualization).

With 64 compute units (4096 stream processors), Radeon Vega Frontier Edition comes with 16 GB of HBM2 graphics memory and will perform in the 13 TFLOP (fp32) performance bracket. Also worth nothing is that the AMD Radeon Vega Frontier Edition uses two PCI-Express 8-pin power connectors, which suggests a power draw north of 300 Watts. The 16GB Radeon Vega Frontier Edition will become available late June 2017.





















