ARM's Latest Mali-T658 GPU Comes To Boost Graphics Performance Of Mobile Devices and Smart-TVs
ARM today announced the ARM Mali-T658 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) - the latest member of the Midgard architecture-based GPU family targeting high performance devices, such as superphones, tablets and smart-TVs.
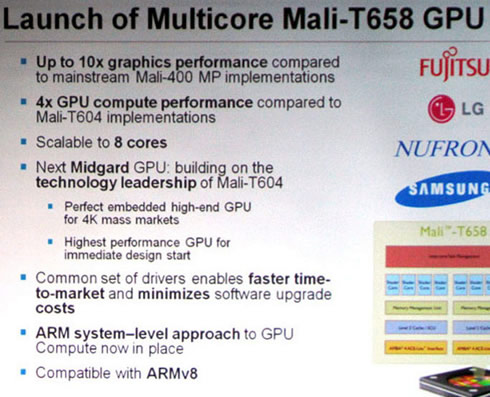
The Mali-T658 graphics processor can be equipped with up to eight cores to help it deliver ten times the graphics performance of the company's existing GPU.
The GPU leverages the ARM system-level approach to multicore design that optimizes both performance and energy-efficiency. ARM claims that the Mali-T658 GPU delivers up to ten times the graphics performance of the Mali-400 MP GPU, found in smartphones from Samsung Electronics, including the Galaxy S II and the new Galaxy Note. It also features four times the GPU Compute performance of the Mali-T604 GPU, enabling a raft of new use-cases outside of traditional graphics processing, including computational photography, image-processing and augmented reality.
Supported by ARM Partners, such as Fujitsu Semiconductor, LG Electronics, Nufront and Samsung, the Mali-T658 GPU extends ARM performance leadership with scalability up to eight cores, and by doubling of the number of arithmetic pipelines within each of these cores. It is also compatible with the ARMv8 architecture.
According to the slide set distributed by ARM to accompany its announcement of the Mali-T658 graphics core, Intel is included as a semiconductor partner within the "Mali graphics ecosystem." The situation is surprising given Intel's competitive position with ARM on general purpose processor technology and because Intel is thought to have an internal graphics development capability.
The ARM Mali-T658 GPU supports a wide range of graphics and compute APIs, including Microsoft DirectX 11, Khronos OpenGL ES, OpenVG, Khronos OpenCL, Google Renderscript and Microsoft DirectCompute.
The Mali-T658 has been designed to work with the ARM Cortex-A15 and Cortex-A7 processors either in standalone modes or in big.LITTLE processing mode. The autonomous nature of the Mali Job Manager, and its ability to carry on graphics processing with a reduced load on the CPU, means it is very well suited to work alongside a big.LITTLE CPU system. By using the right processor for the right task the Mali-T658 is able to handle GPU compute tasks in parallel with the CPU handling the always-on always-connected tasks.
Cache coherency is essential in multicore computing devices to maintain the consistency of data stored in local caches of a shared resource. This ensures optimum performance and energy-efficiency of complex heterogeneous SoC designs, and is designed to address next generation computing devices. ARM system IP, such as CoreLink, enables system level cache coherency across clusters of multicore processors, including the Cortex-A15 MPCore processors and Mali-T658 graphics processors.
Smartphones based on the Mali-T604 GPU will arrive next year, while products that use a Mali-T658 chip with four cores will arrive in 2013. Products powered by a version with the maximum eight cores are expected to be introduced in 2015.

Supported by ARM Partners, such as Fujitsu Semiconductor, LG Electronics, Nufront and Samsung, the Mali-T658 GPU extends ARM performance leadership with scalability up to eight cores, and by doubling of the number of arithmetic pipelines within each of these cores. It is also compatible with the ARMv8 architecture.
According to the slide set distributed by ARM to accompany its announcement of the Mali-T658 graphics core, Intel is included as a semiconductor partner within the "Mali graphics ecosystem." The situation is surprising given Intel's competitive position with ARM on general purpose processor technology and because Intel is thought to have an internal graphics development capability.

The ARM Mali-T658 GPU supports a wide range of graphics and compute APIs, including Microsoft DirectX 11, Khronos OpenGL ES, OpenVG, Khronos OpenCL, Google Renderscript and Microsoft DirectCompute.
The Mali-T658 has been designed to work with the ARM Cortex-A15 and Cortex-A7 processors either in standalone modes or in big.LITTLE processing mode. The autonomous nature of the Mali Job Manager, and its ability to carry on graphics processing with a reduced load on the CPU, means it is very well suited to work alongside a big.LITTLE CPU system. By using the right processor for the right task the Mali-T658 is able to handle GPU compute tasks in parallel with the CPU handling the always-on always-connected tasks.
Cache coherency is essential in multicore computing devices to maintain the consistency of data stored in local caches of a shared resource. This ensures optimum performance and energy-efficiency of complex heterogeneous SoC designs, and is designed to address next generation computing devices. ARM system IP, such as CoreLink, enables system level cache coherency across clusters of multicore processors, including the Cortex-A15 MPCore processors and Mali-T658 graphics processors.
Smartphones based on the Mali-T604 GPU will arrive next year, while products that use a Mali-T658 chip with four cores will arrive in 2013. Products powered by a version with the maximum eight cores are expected to be introduced in 2015.