MIT's Cheetah Robot Can Do a Backflip
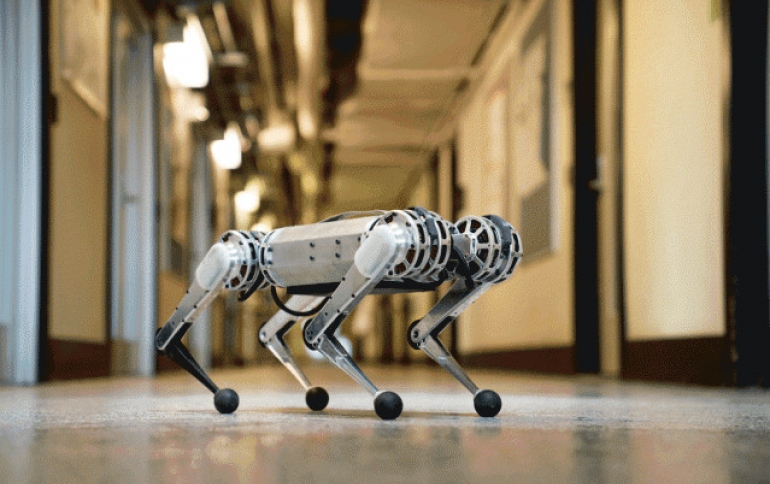
MIT has developed a new mini cheetah robot that is springy and light on its feet, with a range of motion that rivals a champion gymnast.
The four-legged powerpack can bend and swing its legs wide, enabling it to walk either right-side up or upside down. The robot can also trot over uneven terrain about twice as fast as an average person’s walking speed.
Weighing in at just 20 pounds, the limber quadruped is no pushover: When kicked to the ground, the robot can quickly right itself with a swift, kung-fu-like swing of its elbows.
Perhaps most impressive is its ability to perform a 360-degree backflip from a standing position. Researchers claim the mini cheetah is designed to be “virtually indestructible,” recovering with little damage, even if a backflip ends in a spill.
The robot can also trot over uneven terrain about twice as fast as an average person's walking speed.
In the event that a limb or motor does break, the mini cheetah is designed with modularity in mind: Each of the robot’s legs is powered by three identical, low-cost electric motors that the researchers engineered using off-the-shelf parts. Each motor can easily be swapped out for a new one.
Each of the robot’s 12 motors is about the size of a Mason jar lid, and consists of: a stator, or set of coils, that generates a rotating magnetic field; a small controller that conveys the amount of current the stator should produce; a rotor, lined with magnets, that rotates with the stator’s field, producing torque to lift or rotate a limb; a gearbox that provides a 6:1 gear reduction, enabling the rotor to provide six times the torque that it normally would; and a position sensor that measures the angle and orientation of the motor and associated limb.
Each leg is powered by three motors, to give it three degrees of freedom and a huge range of motion. The lightweight, high-torque, low-inertia design enables the robot to execute fast, dynamic maneuvers and make high-force impacts on the ground without breaking gearboxes or limbs.
“You could put these parts together, almost like Legos,” says lead developer Benjamin Katz, a technical associate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering.
The researchers will present the mini cheetah’s design at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, in May. They are currently building more of the four-legged machines, aiming for a set of 10, each of which they hope to loan out to other labs.
The engineers ran the mini cheetah through a number of maneuvers, first testing its running ability through the hallways of MIT’s Pappalardo Lab and along the slightly uneven ground of Killian Court.
In both environments, the quadruped bound along at about 5 miles per hour. The robot’s joints are capable of spinning three times faster, with twice the amount of torque, and Katz estimates the robot could run about twice as fast with a little tuning.
The team wrote another computer code to direct the robot to stretch and twist in various, yoga-like configurations, showcasting its range of motion and ability to rotate its limbs and joints while maintaining balance. They also programmed the robot to recover from an unexpected force, such as a kick to the side. When the researchers kicked the robot to the ground, it automatically shut down.
When it receives a signal to restart, the robot first determines its orientation, then performs a preprogrammed crouch or elbow-swing maneuver to right itself on all fours.
Meanwhile, the MIT team is developing another, even higher-impact maneuver.
“We’re working now on a landing controller, the idea being that I want to be able to pick up the robot and toss it, and just have it land on its feet,” Katz says. “Say you wanted to throw the robot into the window of a building and have it go explore inside the building. You could do that.”