OCZ DDR2 PC2-4200 Gold GX XTC Dual Channel
3. SiSoftware Sandra 2005
Review Pages
 SiSoftware Sandra is a 32 and 64-bit Windows system analyser that includes benchmarking, testing and listing modules. It tries to go beyond other utilities to show you more of what is really going on under the hood so you draw comparisons at both a high and low-level in a single product.
SiSoftware Sandra is a 32 and 64-bit Windows system analyser that includes benchmarking, testing and listing modules. It tries to go beyond other utilities to show you more of what is really going on under the hood so you draw comparisons at both a high and low-level in a single product.
You can get information about the CPU, chipset, video adapter, ports, printers, sound card, memory, network, Windows internals, AGP, ODBC Connections, USB2, Firewire etc. You can save/print/fax/e-mail/post/upload or insert into ADO/ODBC databases reports in text, HTML, XML, SMS/DMI or RPT format.
This version supports multiple sources of information gathering including: remote computers, PDAs, Smart Phones, ADO/ODBC databases or saved system reports. All benchmarks are optimised for both SMP & SMT (Hyper-Threading), up to 32/64 CPUs depending on the platform.
Memory Bandwidth Benchmark
Tests how your memory sub-system compares to other systems with the same or similar memory in other systems. The benchmark is based on the well-known STREAM memory bandwidth benchmark. (Higher is better, i.e. better performance).

The lower timings, from 4-4-4-12 to 3-3-3-12, with the same memory speed at 533 MHz, reported better performance. So even if you don't want to overclock your system and change the memory speed, you'll still gain by simply lowering the timings. But setting the memory frequency to 701 MHz will boost the performance greatly.
Cache & Memory Benchmark
Tests how your CPU cache and memory sub-system(s) compares to other systems with the same or similar CPU & memory in other systems. The benchmark is based on the Memory Bandwidth Benchmark test.
Combined Index: is a composite figure representing the overall performance rating of the entire Cache-Memory performance in terms of MB/s. The value is the logarithmic average of all the results for the entire address space. (Higher is better, i.e. better performance)
For block sizes that could not been tested - the average of previous blocks is used, thus the size of the memory (as long as it is not comparable to largest cache size) is not significant; all cache sizes are significant - larger caches will result in a higher index.

Same results here also. Lowering the timings initially makes a difference, but overclocking does so even more.
Speed Factor: is a figure representing the speed differential between the CPU’s cache and memory. The value is the ratio of the fastest cache (i.e. L1) bandwidth to the main memory bandwidth. (Lower is better, i.e. the memory is not very much slower than the CPU’s cache).
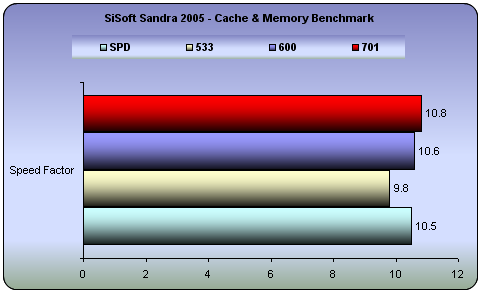
The default memory frequency and 3-3-3-12 timings yield better results.
Review Pages