Researchers Create "Poor-man's q-bit" Device Based on Spintronics That Solves Quantum Problems at Room Temperature
Researchers have created an unconventional spintronics computing scheme harnessing thermal fluctuations and showed a proof-of-concept for probabilistic computing.
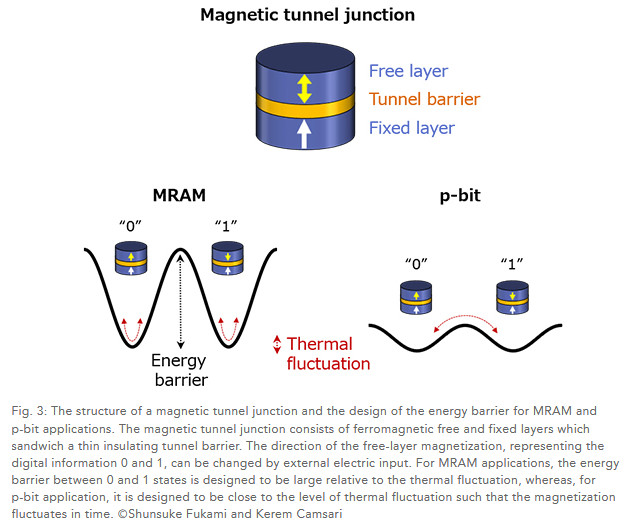
Probabilistic computing using probabilistic bits, or p-bits, whose state fluctuates in time between 0 and 1 has analogies to quantum computing that uses superposition of 0 and 1 of quantum bits, or q-bits.
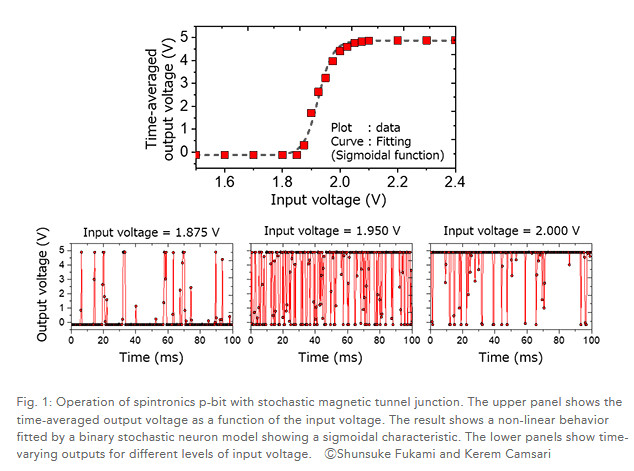
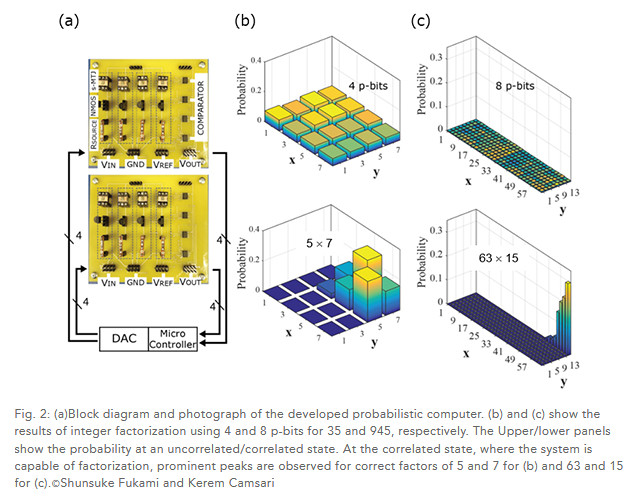
Research groups from Tohoku University and Purdue University developed a spintronics-based p-bit with a stochastic magnetic tunnel junction (s-MTJ) and constructed a rudimentary probabilistic computer inspired by concepts from asynchronous neural networks. Using the developed spintronics probabilistic computer, integer factorization was tested as an illustrative example of optimization problems.
For the operation, a modified algorithm of quantum annealing was applied and up to 4-body interactions were implemented. They succeeded in factorizing 35 into 5 and 7 by 4 p-bits, 161 into 23 and 7 by 6 p-bits, and 945 into 63 and 15 by 8 p-bits.
Quantum computing is expected to execute difficult classes of problems such as optimization that classical computers cannot address efficiently. Whereas most q-bits operate at extremely low temperature and often interact only with neighboring q-bits, the spintronics p-bits can be used like q-bits but operating at room temperature with the ability to correlate, by electrical means, with multiple p-bits even at long distances. In addition, spintronics p-bits can be realized by slightly modifying a matured nonvolatile memory (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory; MRAM) technology, whose integration densities are well above the megabit range. In this sense, the developed p-bit can be regarded as a "poor man's q-bit."
The demonstrated computing scheme based on spintronics technology is particularly attractive for certain classes of problems where approximate solutions are acceptable, because the probabilistic computer makes use of natural stochasticity of s-MTJ instead of introducing it artificially into a deterministic computer. Compared with quantum computers, the spintronics probabilistic computers are attractive in terms of room-temperature operation, ease of implementing many-body interactions, and maturity of fundamental technology in the MRAM community. In this context, the results shown are promising in that they pave an unexplored pathway towards a new computing paradigm that is particularly well-suited for certain classes of problems like optimization and thus is useful in areas such as drug research, encryption and cybersecurity, financial services, data analysis, and supply chain logistics.