Intel And HP Unveil Latest Itanium Server Technology
Intel and HP held a news conference on Thursday announcing the
availability of the newest version of Itanium processors, and
introducing new HP servers.
Intel claims that the Intel Itanium processor 9500 series -
Codenamed Paulson - is more than twice as powerful as the
previous generation, making it ideal for demanding workloads,
including business analytics, database, and large-scale
enterprise resource planning (ERP) applications.
"Built on a new microarchitecture and providing breakthrough performance, the Intel Itanium 9500 processor family signals Intel's ongoing commitment to deliver unparalleled reliability, availability and scalability to meet the critical application demands across all industries," said Diane Bryant, vice president and general manager of Intel's Datacenter and Connected Systems Group.
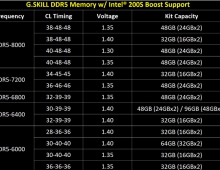
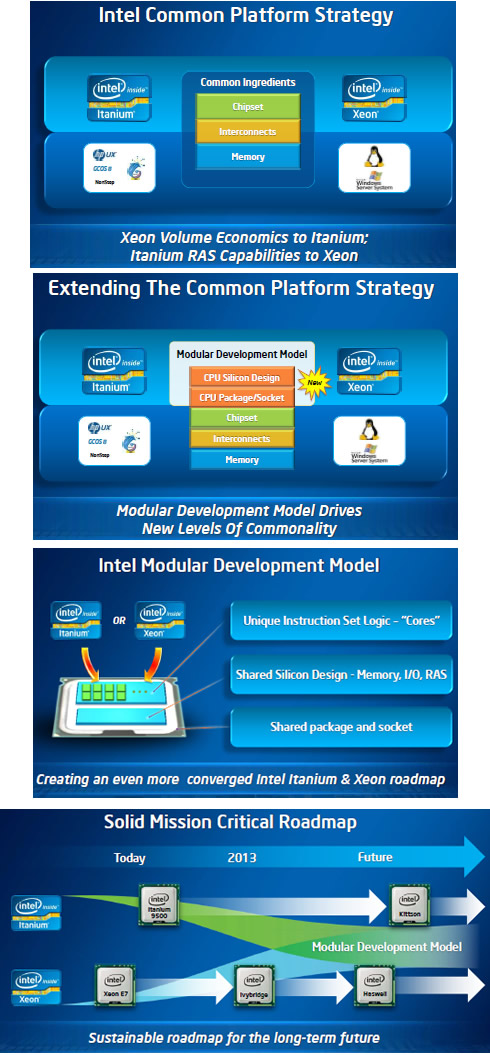
The Intel Itanium processor 9500 series is Intel's most sophisticated general purpose processors to date, containing 3.1 billion transistors. It supports up to twice as many cores (8 instead of 4) than the previous-generation processor, packs up to 54 MB of on-die memory, and enables up to 2 TB of low voltage DIMMs in a four-socket configuration. The speed of the processor increased 40 percent over the previous generation in lower power configurations. The new frequencies range from 1.73 GHz and a power level of 130 watts, to 2.53 GHz at a power level of 170 watts.
Basic features of the new Itanium processor include:
- Up to 8 cores and 16 threads per socket with Intel Hyper-Threading Technology, enhanced with dual-domain multithreading
- New Intel Itanium Processor 9500 Series Microarchitecture (Poulson): Boosts parallelism at all levels with advanced EPIC architecture, including the ability to retire up to 12 instructions per cycle per core, to improve performance on multiple applications/user environments and data-demanding workloads, while enabling denser data center deployments.
- Large addressable memory to 1024 Terabytes
- Up to 54 MB total cache; 32 MB last-level cache
- Intel Itanium New-Instructions
- Intel Instruction Replay Technology: Improves on Intel Itanium's RAS capabillities for higher availability and data integrity.
- Complete Machine Check Architecture, with firmware first error handling: Delivers intelligent handling of multiple classes of rare errors to minimize service interruption and increases system level resiliency.
- Intel Cache Safe Technology: Enables predictive error handling to safeguard against persistent cache errors.
- End-to-end error detection
- Intel Virtualization Technology: Enables 3rd generation virtualization extensions for better workload isolation, reduced latency and less overhead when consolidating application in virtualized environments.
- Directory-based Cache Coherency: Improves cache efficiency and lowers inter-system communication overhead for better scalability in large SMP configurations.
- Intel Turbo Boost Technology, featuring sustained boost: Delivers power to areas where it is needed most to achieve higher performance for all workloads, with better thermal envelop utilization.
- Demand Based Switching: Dynamically optimizes voltage and frequency to reduce energy consumption during typical CPU utilization to reduce energy costs.

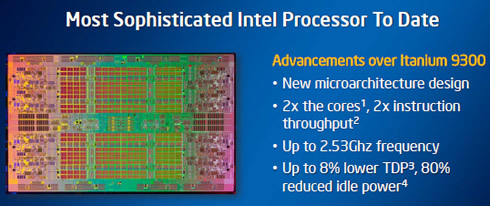
In 2010, Intel introduced its common platform strategy that allows Intel Itanium and Intel Xeon processors to utilize common platform ingredients including chipsets, interconnects and memory. This strategy gives Intel the ability to cascade the strength of Intel Itanium RAS features to benefit the Intel Xeon processor E7 family, and allows Intel Itanium to further extract the efficiencies and value of higher volume economics. For the next-generation Intel Itanium product family, code-named "Kittson," Intel plans to employ an innovative model for Intel Itanium and Intel Xeon development called "Modular Development Model." The model will extend the common platform strategy by sharing silicon-level design elements and socket compatibility. The result for Intel is an even more sustainable path to bring future Itanium processors to market.
Intel Itanium processors continue to maintain industry support among systems makers such as Bull, Hitachi, HP, Inspur and NEC. Enterprise applications are available from multiple vendors, such as, Oracle, SAP, SAS, Sybase and Temenos, among other vendors.
The new HP designs based on the Itanium chips include upgrade boards for its Superdome 2 high-end server. The new CPUs double the number of cores on previous Superdome versions that used 16 or 32 Itanium 9300 CPUs, supporting PCI Express Gen 2 and 10 Gbit/second Ethernet.
HP also released three new Itanium 9500 server boards for its existing BladeSystem c-Class chassis as well as a low-end Itanium 9500 server for branch offices. The BladeSystem boards support two, four and eight CPUs.
The Intel Itanium processor 9500 series is available now and is priced from $1,350 to $4,650 in quantities of 1,000 units.
Itanium suffered a series of setbacks and was eventually overtaken by 64-bit chips based on Intel's x86 architecture. Software created for x86 servers is not compatible with Itanium servers, which are mostly sold by HP.
The future of servers built with Itanium chips was thrown into doubt last year due to a legal battle between long-time partners HP and Oracle and it remains unclear to some experts even after a California state court judge ruled in favor of HP.
In August, a California state court judge ruled in favor of HP and against Oracle over the latter's decision to end support for servers HP makes using Itanium chips.
Oracle has since said it would support Itanium servers.
HP said it would keep offering its customers choices between servers based on heavy-duty Itanium chips and Intel's more widely used "x86" chips.

"Built on a new microarchitecture and providing breakthrough performance, the Intel Itanium 9500 processor family signals Intel's ongoing commitment to deliver unparalleled reliability, availability and scalability to meet the critical application demands across all industries," said Diane Bryant, vice president and general manager of Intel's Datacenter and Connected Systems Group.
The Intel Itanium processor 9500 series is Intel's most sophisticated general purpose processors to date, containing 3.1 billion transistors. It supports up to twice as many cores (8 instead of 4) than the previous-generation processor, packs up to 54 MB of on-die memory, and enables up to 2 TB of low voltage DIMMs in a four-socket configuration. The speed of the processor increased 40 percent over the previous generation in lower power configurations. The new frequencies range from 1.73 GHz and a power level of 130 watts, to 2.53 GHz at a power level of 170 watts.
Basic features of the new Itanium processor include:
- Up to 8 cores and 16 threads per socket with Intel Hyper-Threading Technology, enhanced with dual-domain multithreading
- New Intel Itanium Processor 9500 Series Microarchitecture (Poulson): Boosts parallelism at all levels with advanced EPIC architecture, including the ability to retire up to 12 instructions per cycle per core, to improve performance on multiple applications/user environments and data-demanding workloads, while enabling denser data center deployments.
- Large addressable memory to 1024 Terabytes
- Up to 54 MB total cache; 32 MB last-level cache
- Intel Itanium New-Instructions
- Intel Instruction Replay Technology: Improves on Intel Itanium's RAS capabillities for higher availability and data integrity.
- Complete Machine Check Architecture, with firmware first error handling: Delivers intelligent handling of multiple classes of rare errors to minimize service interruption and increases system level resiliency.
- Intel Cache Safe Technology: Enables predictive error handling to safeguard against persistent cache errors.
- End-to-end error detection
- Intel Virtualization Technology: Enables 3rd generation virtualization extensions for better workload isolation, reduced latency and less overhead when consolidating application in virtualized environments.
- Directory-based Cache Coherency: Improves cache efficiency and lowers inter-system communication overhead for better scalability in large SMP configurations.
- Intel Turbo Boost Technology, featuring sustained boost: Delivers power to areas where it is needed most to achieve higher performance for all workloads, with better thermal envelop utilization.
- Demand Based Switching: Dynamically optimizes voltage and frequency to reduce energy consumption during typical CPU utilization to reduce energy costs.

In 2010, Intel introduced its common platform strategy that allows Intel Itanium and Intel Xeon processors to utilize common platform ingredients including chipsets, interconnects and memory. This strategy gives Intel the ability to cascade the strength of Intel Itanium RAS features to benefit the Intel Xeon processor E7 family, and allows Intel Itanium to further extract the efficiencies and value of higher volume economics. For the next-generation Intel Itanium product family, code-named "Kittson," Intel plans to employ an innovative model for Intel Itanium and Intel Xeon development called "Modular Development Model." The model will extend the common platform strategy by sharing silicon-level design elements and socket compatibility. The result for Intel is an even more sustainable path to bring future Itanium processors to market.

Intel Itanium processors continue to maintain industry support among systems makers such as Bull, Hitachi, HP, Inspur and NEC. Enterprise applications are available from multiple vendors, such as, Oracle, SAP, SAS, Sybase and Temenos, among other vendors.
The new HP designs based on the Itanium chips include upgrade boards for its Superdome 2 high-end server. The new CPUs double the number of cores on previous Superdome versions that used 16 or 32 Itanium 9300 CPUs, supporting PCI Express Gen 2 and 10 Gbit/second Ethernet.
HP also released three new Itanium 9500 server boards for its existing BladeSystem c-Class chassis as well as a low-end Itanium 9500 server for branch offices. The BladeSystem boards support two, four and eight CPUs.
The Intel Itanium processor 9500 series is available now and is priced from $1,350 to $4,650 in quantities of 1,000 units.

Itanium suffered a series of setbacks and was eventually overtaken by 64-bit chips based on Intel's x86 architecture. Software created for x86 servers is not compatible with Itanium servers, which are mostly sold by HP.
The future of servers built with Itanium chips was thrown into doubt last year due to a legal battle between long-time partners HP and Oracle and it remains unclear to some experts even after a California state court judge ruled in favor of HP.
In August, a California state court judge ruled in favor of HP and against Oracle over the latter's decision to end support for servers HP makes using Itanium chips.
Oracle has since said it would support Itanium servers.
HP said it would keep offering its customers choices between servers based on heavy-duty Itanium chips and Intel's more widely used "x86" chips.