
Nantero's Next-Generation Memory NRAM Could Replace DRAM, SSDs
A new fast, high density memory called NRAM (non-volatile random access memory) developed by Nantero, can enable a variety of new features and products in both consumer and enterprise electronics. The NRAM leverages research in nanotechnology and the use of carbon nanotube technology (CNT). Considered one of the strongest materials known to man, CNTs possess structural and electrical properties that make it ideal for delivering a new generation of faster, high-dense and extremely low power memory. With one CNT being just 1/50,000th the diameter of a human hair, these tiny cylinders are 50 times stronger than steel, half the density of aluminum, and have better thermal and electrical conductivity properties than any other material scientists are aware of today.

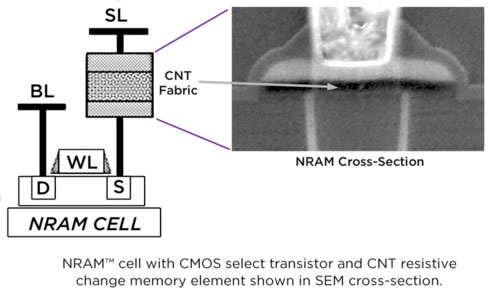
NRAM is based on forming a film of CNTs that are deposited onto a standard silicon substrate that contains an underlying cell select device and array lines (typically transistors or diodes) that interface the NRAM switch.
The NRAM acts as a resistive non-volatile random access memory NVRAM and can be placed in two or more resistive modes depending on the resistive state of the CNT fabric. When the CNTs are not in contact the resistance state of the fabric is high and represents a "0" state. When the CNTs are brought into contact, the resistance state of the fabric is low and represents a "1" state.
Nantero’s NRAM is as fast as and denser than DRAM, nonvolatile like flash, has essentially zero power consumption in standby mode and 160x lower write energy per bit than flash, and is highly resistant to environmental forces (heat even up to 300 degrees C, cold, magnetism, radiation, vibration). NRAM promises to retain memory for >1,000 years at 85 degrees Celsius or more than 10 years at 300 degrees Celsius. The memory is compatible with existing CMOS fabs without needing any new tools or processes, and it is scalable even to below 5nm. Given that it requires a small number of process steps and only one mask layer, NRAM can be fabricated at low cost, and is compatible with both 3D multilayer architectures and MLC operation.
Nantero, has recently closed a $31.5 million Series E financing round, which included new investors and participation from existing investors Charles River Ventures, Draper Fisher Jurvetson, Globespan Capital Partners, and Harris & Harris Group.
The company is already licensing its NRAM IP to major chip manufacturers, foundries and electronics companies around the world. NRAM has already been installed in multiple production fabs and is currently being designed into new electronic products.
However, Nantero faces challenges from other emerging memory types and developments in the fast-changing computing landscape.
Possible DRAM and NAND flash replacements like RRAM (resistive RAM) and MRAM (magnetoresistive RAM) are already being used on a limited basis, and phase-change memory (PCM) -- backed by IBM and Samsung -- is still being refined.
















