
Researchers Say Silicon Nanosheets is the Path to 5nm Transistors
IBM, its Research Alliance partners GLOBALFOUNDRIES and Samsung, and equipment suppliers have developed a process to build silicon nanosheet transistors that they believe will enable 5 nanometer (nm) chips.
The details of the process will be presented at the 2017 Symposia on VLSI Technology and Circuits conference in Kyoto, Japan. In less than two years since developing a 7nm test node chip with 20 billion transistors, scientists have paved the way for 30 billion switches on a fingernail-sized chip.
The resulting increase in performance will help accelerate cognitive computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and other data-intensive applications delivered in the cloud. The power savings could also mean that the batteries in smartphones and other mobile products could last two to three times longer than today's devices, before needing to be charged.
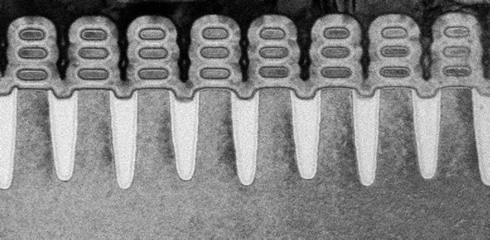
Scientists working as part of the IBM-led Research Alliance at the SUNY Polytechnic Institute Colleges of Nanoscale Science and Engineering's NanoTech Complex in Albany, NY achieved the breakthrough by using stacks of silicon nanosheets as the device structure of the transistor, instead of the standard FinFET architecture, which is the blueprint for the semiconductor industry up through 7nm node technology.
"For business and society to meet the demands of cognitive and cloud computing in the coming years, advancement in semiconductor technology is essential," said Arvind Krishna, senior vice president, Hybrid Cloud, and director, IBM Research. "That's why IBM aggressively pursues new and different architectures and materials that push the limits of this industry, and brings them to market in technologies like mainframes and our cognitive systems."
Compared to the leading edge 10nm technology available in the market, a nanosheet-based 5nm technology can deliver 40 percent performance enhancement at fixed power, or 75 percent power savings at matched performance. This improvement enables a significant boost to meeting the future demands of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, virtual reality and mobile devices.
This work is the first to demonstrate the feasibility to design and fabricate stacked nanosheet devices with electrical properties superior to FinFET architecture.
This same Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography approach used to produce the 7nm test node and its 20 billion transistors was applied to the nanosheet transistor architecture. Using EUV lithography, the width of the nanosheets can be adjusted continuously, all within a single manufacturing process or chip design. This adjustability permits the fine-tuning of performance and power for specific circuits - something not possible with today's FinFET transistor architecture production, which is limited by its current-carrying fin height. Therefore, while FinFET chips can scale to 5nm, simply reducing the amount of space between fins does not provide increased current flow for additional performance.





















