Fujitsu Technology Searches Encrypted Data to Maintain Privacy
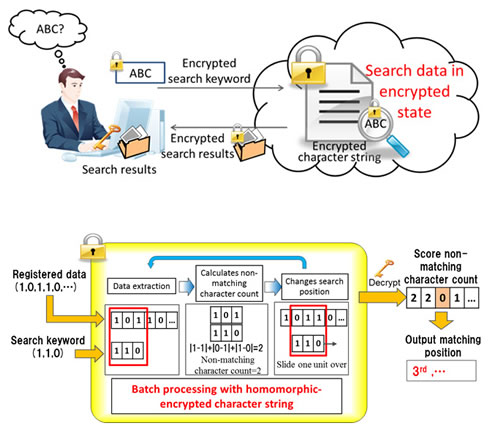
Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a technology that can perform concealed searches of encrypted data in its encrypted form.
Searching data while it is encrypted makes it possible to maintain a high level of privacy with no risk of leaks. Through outsourcing, searches of confidential data can be carried out safely as text data and keyword search terms kept private. Whether or not search hits are obtained also remains undisclosed.
Based on homomorphic encryption which allows computations to be performed on confidential encrypted data without disclosure, Fujitsu has developed a new batch search method that accelerates the processing speed of searching for matches on the encrypted data. The new technology can search 16,000 characters in one second, and does not need an index of searchable keywords to be generated in advance. Instead, it makes discretionary searches of the encrypted text directly for any search key.
This technology makes it possible to search encrypted data for any arbitrary search key, while keeping not only the source data itself encrypted but also the search key and even the search results. When applied to searching for a certain base sequence in a DNA strand, for example, this technology allows for a person's DNA information to remain private while finding whether or not it contains a certain sequence. This will also make it possible to achieve new analytical results obtained from medical records or base sequences collected from multiple hospitals, all while encrypted, which has the potential to make new drug development more efficient. Even data that has particularly sensitive privacy implications, such as medical records, can now be searched in full. The technology has potential applications outside of biology and medicine, as well, such as, for example, in aggregating results from multiple educational institutions for analysis. It could be used in a variety of situations where the privacy of data needs to be protected, or where data protection has been a problem.
Fujitsu Laboratories is continuing with practical testing of this technology, with a goal of commercial implementation in 2015.
Based on homomorphic encryption which allows computations to be performed on confidential encrypted data without disclosure, Fujitsu has developed a new batch search method that accelerates the processing speed of searching for matches on the encrypted data. The new technology can search 16,000 characters in one second, and does not need an index of searchable keywords to be generated in advance. Instead, it makes discretionary searches of the encrypted text directly for any search key.

This technology makes it possible to search encrypted data for any arbitrary search key, while keeping not only the source data itself encrypted but also the search key and even the search results. When applied to searching for a certain base sequence in a DNA strand, for example, this technology allows for a person's DNA information to remain private while finding whether or not it contains a certain sequence. This will also make it possible to achieve new analytical results obtained from medical records or base sequences collected from multiple hospitals, all while encrypted, which has the potential to make new drug development more efficient. Even data that has particularly sensitive privacy implications, such as medical records, can now be searched in full. The technology has potential applications outside of biology and medicine, as well, such as, for example, in aggregating results from multiple educational institutions for analysis. It could be used in a variety of situations where the privacy of data needs to be protected, or where data protection has been a problem.
Fujitsu Laboratories is continuing with practical testing of this technology, with a goal of commercial implementation in 2015.