
AMD's Changes Chip Design Methodology, Updates Roadmaps, Focuses On Tablets And Cloud
At its annual Financial Analyst Day, AMD detailed a
new "ambidextrous" strategy that builds on the
company's long history of x86 and graphics innovation
while embracing other technologies and intellectual
property to deliver differentiated products.
AMD new chief executive Rory Read said the company
would leverage its PC chip technology to attack the
fast-growing tablet segment as well as emerging
markets but stay away from the smartphone market.
"We're going to double down on client and mobility ... I'm not suggesting we dive into smartphones, a heavily crowded space with low margins ... I'm going to focus on client mobility, thin and light," Read said.
AMD plans to adopt an SoC-centric roadmap designed to speed time-to-market, drive sustained execution, and enable the development of more tailored solutions. AMD says that SoC design methodology is advantageous because it is a modular approach to processor design, leveraging best practice tools and microprocessor design flows with the ability to easily re-use IP and design blocks across a range of products.
"AMD's strategy capitalizes on the convergence of technologies and devices that will define the next era of the industry," said Rory Read. "The trends around consumerization, the Cloud and convergence will only grow stronger in the coming years. AMD has a unique opportunity to take advantage of this key industry inflection point. We remain focused on continuing the work we began last year to re-position AMD. Our new strategy will help AMD embrace the shifts occurring in the industry, marrying market needs with innovative technologies and become a consistent growth engine."
Read said AMD would focus on opportunities in cloud computing and growing demand from developing countries like China for entry level PCs and other devices.
Facing problems manufacturing a newly launched 32 nanometer PC chip, Read in November announced he was slashing 10 percent of AMD's workforce to save about $200 million in annual operating costs.
AMD Chief Financial Officer Thomas Siefert told analysts on Thursday he expects gross margins in 2012 between 44 percent and 48 percent. AMD in the fourth quarter had a gross margin of 46 percent.
AMD has long struggled to keep up with much larger Intel in powerful PC processors. It and Intel now face challenges from companies like Qualcomm that are planning to make low-end PC chips using power-sipping technology licensed to them by ARM Holdings.
New product roadmaps
Additionally, AMD today announced updates to its product roadmaps for AMD Central Processing Unit (CPU) and Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) products it plans to introduce in 2012 and 2013. The roadmap modifications address priorities across form factors including ultrathin notebooks, tablets, all-in-ones, desktops and servers with a clear focus on low power, emerging markets and the Cloud.

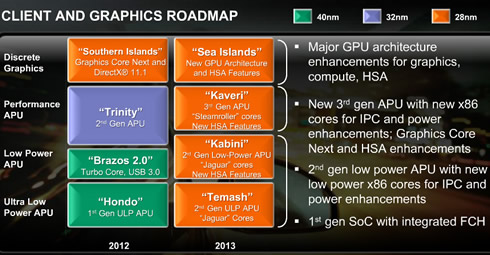
AMD's updated product roadmap features second generation mainstream ("Trinity") and low-power ("Brazos 2.0") APUs for notebooks and desktops; "Hondo," an APU specifically designed for tablets; new CPU cores in 2012 and 2013 with "Piledriver" and its successor "Steamroller," as well as "Jaguar," which is the successor to AMD's "Bobcat" core. In 2012, AMD plans to introduce four new AMD Opteron processors.
"Brazos 2.0" Accelerated Processor Unit (APU) family will be used for essential desktop and notebook, netbook, tablet, all-in-one and small desktop form factors. AMD will add plenty of new features to the "Brazos 2.0" APU family, including increased CPU and GPU performance, longer battery life, a bevy of integrated I/O options and improvements to AMD Steady Video technology. "Brazos 2.0" is scheduled to hit the market in the first half of 2012.
AMD's "Trinity" APU for desktop and notebook remains on track for introduction in mid-2012, with plans to pack up to four "Piledriver" CPU cores and next-generation DirectX 11-capable graphics technology, together delivering up to 50% more compute performance than AMD's "Llano" offerings, including superior entertainment potential, longer battery-life and HD graphics.
New for 2012, AMD will introduce a low voltage "Trinity" APU that will be aimed at next-generation of ultrathin notebook. This "Trinity" APU matches the experience enabled by the AMD 2011 APU in up to half the TDP. "Trinity"is on track for introduction in mid-2012.
In 2012 AMD will also introduce the ultra-low voltage "Hondo" APU for tablets. These low-power (power maxes out at 5W TDP) APUs will have "Bobcat" CPU cores and support DirectX 11 technology in a BGA or pin-less, thin processor package. Look for these in the second half of 2012.
On the desktop platform side of things, the "Vishera" CPU will replace the "Komodo" CPU for desktop. This change enables accelerated time to market for improved performance and next-generation CPU features while maintaining the existing AM3+ motherboards. The "Vishera" CPU ushers in many updates, includes 8 "Piledriver" cores, and when compared with the previous generation, provides higher frequencies, improved instruction per clock performance, advanced instruction sets (thus increasing application performance), additional DDR3 memory support and next-generation AMD Turbo Core Technology. AMD plans to launch "Vishera" in the second half of 2012.
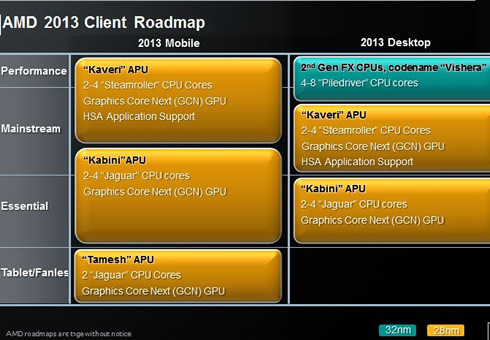
2013 brings evolution to AMD's client roadmaps including moving its low power APUs to a system on a chip (SoC) design with the AMD Fusion Controller Hub integrated right into a single chip design.
In the performance APU category our third-generation APU, "Kaveri," will employ "Steamroller" (the evolution of AMD's "Piledriver"core architecture) x86 cores for enhanced instructions per clock and power advantages. "Kaveri" will also be AMD's first Teraflop-class APU.
"Applications that take advantage of GPU accelerate will give users an amazing experience thanks to our Graphics Core Next and new Heterogeneous Systems Architecture (HSA) enabling features for easier programming of accelerated processing capabilities," AMD said.
AMD's new chip design called Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA) which enables software developers to program APUs by combining scalar processing on the CPU with parallel processing on the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), all while providing high bandwidth access to memory at low power. AMD is working to make HSA an open industry standard for the developer community.

HSA will reach maturity by 2014 with 64-bit addressing, virtual memory, better internal bandwidth and software taking advantage of both processing units, AMD said. A chip code-named Kabini for low-power laptops due in 2013 will see HSA at work.
In the low power category, the "Kabini" SoC APU takes over for "Brazos 2.0." This second generation low power APU integrates "Jaguar" x86 cores for augmented performance and energy efficiency. These APUs will also benefit from select HSA features and functionality.
AMD's second generation, ultra-low-power "Temash" SoC APU will follow "Hondo" for tablet and other fanless form factors. This APU will also leverage the "Jaguar" low-power x86 cores and HSA features.
AMD also changed its server roadmaps. The company's previous roadmap featured two CPUs for later this year; the 20-core "Terramar" and the 10-core "Sepang." These were going to be in all new platforms/socket infrastructures. AMD says that that would potentially have caused a disruption in the data center and more complexity in managing multiple generations of platforms. Instead, AMD says it found new a way to deliver better performance than it was expecting in those platforms, but still do it in the same G34 and C32 packages as today's AMD Opteron 4000 and 6000 Series processors.
This means AMD's customers will be able to the next generation processors, code named "Abu Dhabi" and "Seoul," and still continue to buy the same platforms that they have been deploying. The same platforms can be used with AMD Opteron 6100 Series, 6200 Series and the upcoming "Abu Dhabi" processors or the AMD Opteron 4100 Series, 4200 Series and upcoming "Seoul" processors. Core counts will remain the same, but the overall performance will take a jump.

And because these drop into the same platform, the thermals stay consistent because these upcoming processors need to live in the same platform power requirements as their predecessors.
AMD claims that it managed to get more performance in the same core counts, through the integration of the "Piledriver" core, AMD's next generation CPU core. As you will recall, the AMD Opteron 4200 and 6200 Series processors featured the "Bulldozer" core, and the next evolution of that core is "Piledriver," which adds additional clock frequency and some IPC improvements. Beyond "Piledriver," the next 2 generations of cores will be "Steamroller" and "Excavator." AMD did not disclose what is in these next 2 cores, but expects to continually increase performance and power efficiency.
"Zurich" is the codename of AMD's upcoming single socket server processors. "Zurich" will launch this quarter with the "Bulldozer" core and then be followed up with "Delhi", featuring "Piledriver", around the same time that the other processors pick up the newest core.
Last, but certainly not least, AMD has added the "Sea Islands" family to its graphics roadmap. The company did not gave any additional details, other that it will be released in 2013.
For the Desktop GPUs, AMD has already released the high-end Radeon HD 7900 series (Tahiti). AMD will start shipping the remaining HD 7000 family GPUs - "Pitcairn" and "Cape Verde" for the "preformance" segment as well as an ultra entusiast model later this year.
Next up in AMD's release schedule is Cape Verde, which are expected to appear in the Radeon HD 7750 and HD 7770 next month. Cape Verde is expected to feature 896 SP over 14 CUs and 56 TMU, with a core frequency of 900 MHz in the HD 7770 SKU. HD 7750 will come with 1 CU disabled for a total of 832 SP and 52 TMU. The Cape Verde die will also feature a 128-bit interface.
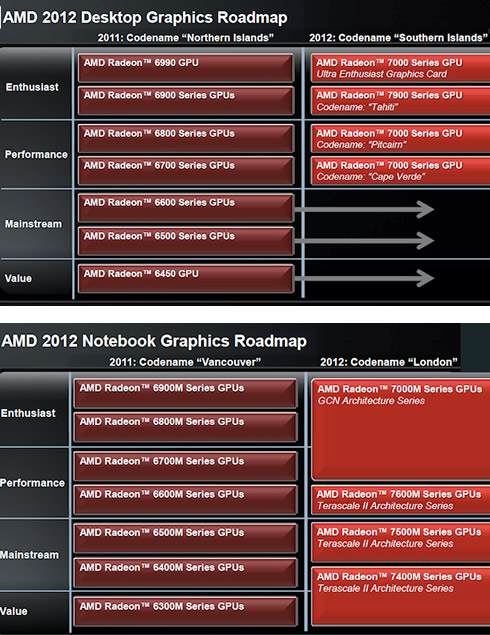
The "Pitcairn" GPUs are expectde to appear sometime in March, with the Radeon HD 7850 and HD 7870. Pitcairn will feature 1408 SP/22 CU/ 88 TMU.
Last but certainly not least, the "New Zealand' dual-GPU is slated for an early Q2 2012 release. New Zealand will be branded HD 7990 and is expected to become AMD's fastest graphics card.
In the mobile GPU merket, the Radeon 7000M series of GPUs codenamed "London" will be released this year. It will include a high-end model based on the GCN architecture, the "performance" HD 7600M, the mainstream 7500M and the "value" 7400M. All these three GPUs will be based on the "Terascale II" architecture.
"We're going to double down on client and mobility ... I'm not suggesting we dive into smartphones, a heavily crowded space with low margins ... I'm going to focus on client mobility, thin and light," Read said.
AMD plans to adopt an SoC-centric roadmap designed to speed time-to-market, drive sustained execution, and enable the development of more tailored solutions. AMD says that SoC design methodology is advantageous because it is a modular approach to processor design, leveraging best practice tools and microprocessor design flows with the ability to easily re-use IP and design blocks across a range of products.
"AMD's strategy capitalizes on the convergence of technologies and devices that will define the next era of the industry," said Rory Read. "The trends around consumerization, the Cloud and convergence will only grow stronger in the coming years. AMD has a unique opportunity to take advantage of this key industry inflection point. We remain focused on continuing the work we began last year to re-position AMD. Our new strategy will help AMD embrace the shifts occurring in the industry, marrying market needs with innovative technologies and become a consistent growth engine."
Read said AMD would focus on opportunities in cloud computing and growing demand from developing countries like China for entry level PCs and other devices.
Facing problems manufacturing a newly launched 32 nanometer PC chip, Read in November announced he was slashing 10 percent of AMD's workforce to save about $200 million in annual operating costs.
AMD Chief Financial Officer Thomas Siefert told analysts on Thursday he expects gross margins in 2012 between 44 percent and 48 percent. AMD in the fourth quarter had a gross margin of 46 percent.
AMD has long struggled to keep up with much larger Intel in powerful PC processors. It and Intel now face challenges from companies like Qualcomm that are planning to make low-end PC chips using power-sipping technology licensed to them by ARM Holdings.
New product roadmaps
Additionally, AMD today announced updates to its product roadmaps for AMD Central Processing Unit (CPU) and Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) products it plans to introduce in 2012 and 2013. The roadmap modifications address priorities across form factors including ultrathin notebooks, tablets, all-in-ones, desktops and servers with a clear focus on low power, emerging markets and the Cloud.

AMD's updated product roadmap features second generation mainstream ("Trinity") and low-power ("Brazos 2.0") APUs for notebooks and desktops; "Hondo," an APU specifically designed for tablets; new CPU cores in 2012 and 2013 with "Piledriver" and its successor "Steamroller," as well as "Jaguar," which is the successor to AMD's "Bobcat" core. In 2012, AMD plans to introduce four new AMD Opteron processors.
"Brazos 2.0" Accelerated Processor Unit (APU) family will be used for essential desktop and notebook, netbook, tablet, all-in-one and small desktop form factors. AMD will add plenty of new features to the "Brazos 2.0" APU family, including increased CPU and GPU performance, longer battery life, a bevy of integrated I/O options and improvements to AMD Steady Video technology. "Brazos 2.0" is scheduled to hit the market in the first half of 2012.
AMD's "Trinity" APU for desktop and notebook remains on track for introduction in mid-2012, with plans to pack up to four "Piledriver" CPU cores and next-generation DirectX 11-capable graphics technology, together delivering up to 50% more compute performance than AMD's "Llano" offerings, including superior entertainment potential, longer battery-life and HD graphics.
New for 2012, AMD will introduce a low voltage "Trinity" APU that will be aimed at next-generation of ultrathin notebook. This "Trinity" APU matches the experience enabled by the AMD 2011 APU in up to half the TDP. "Trinity"is on track for introduction in mid-2012.
In 2012 AMD will also introduce the ultra-low voltage "Hondo" APU for tablets. These low-power (power maxes out at 5W TDP) APUs will have "Bobcat" CPU cores and support DirectX 11 technology in a BGA or pin-less, thin processor package. Look for these in the second half of 2012.
On the desktop platform side of things, the "Vishera" CPU will replace the "Komodo" CPU for desktop. This change enables accelerated time to market for improved performance and next-generation CPU features while maintaining the existing AM3+ motherboards. The "Vishera" CPU ushers in many updates, includes 8 "Piledriver" cores, and when compared with the previous generation, provides higher frequencies, improved instruction per clock performance, advanced instruction sets (thus increasing application performance), additional DDR3 memory support and next-generation AMD Turbo Core Technology. AMD plans to launch "Vishera" in the second half of 2012.

2013 brings evolution to AMD's client roadmaps including moving its low power APUs to a system on a chip (SoC) design with the AMD Fusion Controller Hub integrated right into a single chip design.
In the performance APU category our third-generation APU, "Kaveri," will employ "Steamroller" (the evolution of AMD's "Piledriver"core architecture) x86 cores for enhanced instructions per clock and power advantages. "Kaveri" will also be AMD's first Teraflop-class APU.
"Applications that take advantage of GPU accelerate will give users an amazing experience thanks to our Graphics Core Next and new Heterogeneous Systems Architecture (HSA) enabling features for easier programming of accelerated processing capabilities," AMD said.
AMD's new chip design called Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA) which enables software developers to program APUs by combining scalar processing on the CPU with parallel processing on the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), all while providing high bandwidth access to memory at low power. AMD is working to make HSA an open industry standard for the developer community.

HSA will reach maturity by 2014 with 64-bit addressing, virtual memory, better internal bandwidth and software taking advantage of both processing units, AMD said. A chip code-named Kabini for low-power laptops due in 2013 will see HSA at work.
In the low power category, the "Kabini" SoC APU takes over for "Brazos 2.0." This second generation low power APU integrates "Jaguar" x86 cores for augmented performance and energy efficiency. These APUs will also benefit from select HSA features and functionality.
AMD's second generation, ultra-low-power "Temash" SoC APU will follow "Hondo" for tablet and other fanless form factors. This APU will also leverage the "Jaguar" low-power x86 cores and HSA features.
AMD also changed its server roadmaps. The company's previous roadmap featured two CPUs for later this year; the 20-core "Terramar" and the 10-core "Sepang." These were going to be in all new platforms/socket infrastructures. AMD says that that would potentially have caused a disruption in the data center and more complexity in managing multiple generations of platforms. Instead, AMD says it found new a way to deliver better performance than it was expecting in those platforms, but still do it in the same G34 and C32 packages as today's AMD Opteron 4000 and 6000 Series processors.
This means AMD's customers will be able to the next generation processors, code named "Abu Dhabi" and "Seoul," and still continue to buy the same platforms that they have been deploying. The same platforms can be used with AMD Opteron 6100 Series, 6200 Series and the upcoming "Abu Dhabi" processors or the AMD Opteron 4100 Series, 4200 Series and upcoming "Seoul" processors. Core counts will remain the same, but the overall performance will take a jump.

And because these drop into the same platform, the thermals stay consistent because these upcoming processors need to live in the same platform power requirements as their predecessors.
AMD claims that it managed to get more performance in the same core counts, through the integration of the "Piledriver" core, AMD's next generation CPU core. As you will recall, the AMD Opteron 4200 and 6200 Series processors featured the "Bulldozer" core, and the next evolution of that core is "Piledriver," which adds additional clock frequency and some IPC improvements. Beyond "Piledriver," the next 2 generations of cores will be "Steamroller" and "Excavator." AMD did not disclose what is in these next 2 cores, but expects to continually increase performance and power efficiency.
"Zurich" is the codename of AMD's upcoming single socket server processors. "Zurich" will launch this quarter with the "Bulldozer" core and then be followed up with "Delhi", featuring "Piledriver", around the same time that the other processors pick up the newest core.
Last, but certainly not least, AMD has added the "Sea Islands" family to its graphics roadmap. The company did not gave any additional details, other that it will be released in 2013.

For the Desktop GPUs, AMD has already released the high-end Radeon HD 7900 series (Tahiti). AMD will start shipping the remaining HD 7000 family GPUs - "Pitcairn" and "Cape Verde" for the "preformance" segment as well as an ultra entusiast model later this year.
Next up in AMD's release schedule is Cape Verde, which are expected to appear in the Radeon HD 7750 and HD 7770 next month. Cape Verde is expected to feature 896 SP over 14 CUs and 56 TMU, with a core frequency of 900 MHz in the HD 7770 SKU. HD 7750 will come with 1 CU disabled for a total of 832 SP and 52 TMU. The Cape Verde die will also feature a 128-bit interface.

The "Pitcairn" GPUs are expectde to appear sometime in March, with the Radeon HD 7850 and HD 7870. Pitcairn will feature 1408 SP/22 CU/ 88 TMU.
Last but certainly not least, the "New Zealand' dual-GPU is slated for an early Q2 2012 release. New Zealand will be branded HD 7990 and is expected to become AMD's fastest graphics card.
In the mobile GPU merket, the Radeon 7000M series of GPUs codenamed "London" will be released this year. It will include a high-end model based on the GCN architecture, the "performance" HD 7600M, the mainstream 7500M and the "value" 7400M. All these three GPUs will be based on the "Terascale II" architecture.





















