Samsung Develops First DDR4 DRAM, Using 30nm Class Technology
Samsung announced today that it completed development of the
industry's first DDR4 DRAM module last month, using 30 nanometer (nm) class process technology.
"Samsung has been actively supporting the IT industry with our green
memory initiative by coming up with eco-friendly, innovative memory
products providing higher performance and power efficiency every
year," said Dong Soo Jun, president, memory division, Samsung
Electronics. "The new DDR4 DRAM will build even greater confidence in
our cutting-edge green memory, particularly when we introduce
four-gigabit (Gb) DDR4-based products using next generation process
technology for mainstream application."
The new DDR4 DRAM module can achieve data transfer rates of 2.133 gigabits per second (Gbps) at 1.2V, compared to 1.35V and 1.5V DDR3 DRAM at an equivalent 30nm-class process technology, with speeds of up to 1.6Gbps. When applied to a notebook, it reduces power consumption by 40 percent compared to a 1.5V DDR3 module.
The module makes use of Pseudo Open Drain (POD), a new technology that has been adapted to high-performance graphic DRAM to allow DDR4 DRAM to consume just half the electric current of DDR3 when reading and writing data.
By employing new circuit architecture, Samsung's DDR4 will be able to run from 1.6 up to 3.2Gbps, compared to today's typical speeds of 1.6Gbps for DDR3 and 800Mbps for DDR2.
Late last month, Samsung provided 1.2V 2 gigabyte (2GB) DDR4 unbuffered dual in-line memory modules (UDIMM) to a controller maker for testing.
Samsung now plans to work closely with a number of server makers to help insure completion of JEDEC standardization of DDR4 technologies in the second half of this year.
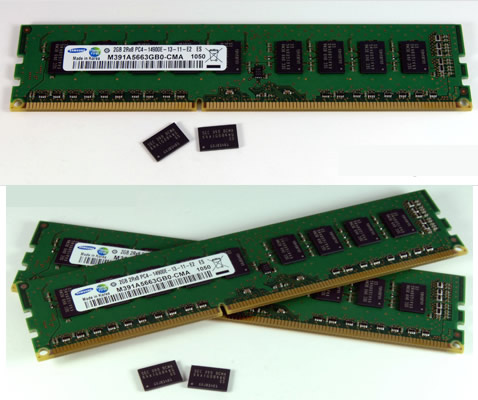
The new DDR4 DRAM module can achieve data transfer rates of 2.133 gigabits per second (Gbps) at 1.2V, compared to 1.35V and 1.5V DDR3 DRAM at an equivalent 30nm-class process technology, with speeds of up to 1.6Gbps. When applied to a notebook, it reduces power consumption by 40 percent compared to a 1.5V DDR3 module.
The module makes use of Pseudo Open Drain (POD), a new technology that has been adapted to high-performance graphic DRAM to allow DDR4 DRAM to consume just half the electric current of DDR3 when reading and writing data.
By employing new circuit architecture, Samsung's DDR4 will be able to run from 1.6 up to 3.2Gbps, compared to today's typical speeds of 1.6Gbps for DDR3 and 800Mbps for DDR2.
Late last month, Samsung provided 1.2V 2 gigabyte (2GB) DDR4 unbuffered dual in-line memory modules (UDIMM) to a controller maker for testing.
Samsung now plans to work closely with a number of server makers to help insure completion of JEDEC standardization of DDR4 technologies in the second half of this year.