Fujitsu Receiver Could Enable Smartphones To Wirelessly Receive 8K HD Video Instantly
Fujitsu Limited and Fujitsu Laboratories have developed a 300 GHz band compact receiver capable of high-speed wireless communications at a rate of several tens of gigabits per second. Radio signals with a frequency greater than 100GHz, called the terahertz band, allow for increases in usable frequency range and communication speed of more than 100 times compared with the 0.8-2.0 GHz range used by current mobile devices.
Fujitsu has developed technology that combines a receiver-amplifier chip and terahertz-band antenna with a low-loss connection. This has made it possible to reduce the receiver's size to one tenth that of previous receivers, making use in mobile devices possible.
Background
As terahertz-band waves attenuate sharply when propagating through space, a highly sensitive receiver is necessary to receive data from weak waves. In recent years, highly sensitive receiver-amplifier chips that work in the terahertz band have been developed by a number of companies, but with the necessity to make the module that mounted the receiver-amplifier chip and the exterior antenna separately, the receivers produced were large and difficult to integrate into mobile devices.
Existing high-sensitivity terahertz-band receivers consist of a receiver-amplifier module and separate antenna, with a specialized component called a waveguide to connect them, which makes for large receivers. The most effective way to miniaturize them is to build the antenna directly into the receiver-amplifier module and eliminate the waveguide. Modules with built-in antennas are built by connecting the antenna and the receiver-amplifier chip through an internal printed-circuit substrate, making a waveguide unnecessary. The problem then is that the most common materials for printed-circuit substrates for high-frequency waves are ceramic, quartz, or Teflon, but when used in the terahertz band, there is significant signal attenuation and loss of receiving sensitivity.
By developing a low-loss technology for connecting terahertz-band antennas with already developed receiver-amplifier chips, Fujitsu has now developed the world's first 300 GHz band receiver with an internal antenna. With a cubic capacity at 0.75 of a centimeter (not including output terminals) it can be installed in mobile devices.
The Japanese company used a polyimide that can be micro-fabricated for the printed-circuit substrate. Signals received by the antenna are transmitted to the receiver-amplifier chip through a connecting circuit. In order to ensure that the terahertz signal is transmitted through the connecting circuit dependably, with low loss, the top and bottom layers of the printed-circuit substrate are grounded, and these layers are connected with electrical lines called through-hole vias. These vias need to be spaced apart by less than one-tenth of the signal's wavelength-in this case, less than a few tens of microns-in order for the radio waves to be transmitted properly. While polyimide as a material has a 10% higher loss than quartz, because its processing accuracy is more than four times higher, the through-hole vias can be placed within several tens of microns of each other, halving the loss as compared to a connecting circuit on a quartz printed circuit.
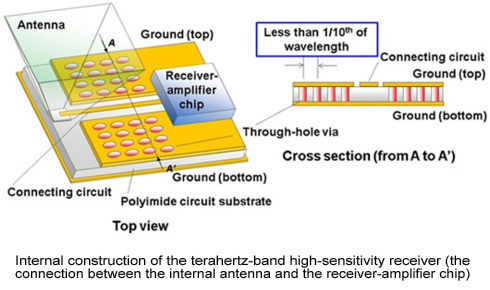
In order to transmit the received signal from the connecting circuit on the printed-circuit substrate to the receiver-amplifier chip with low loss, Fujitsu developed mounting technology that faces the circuit-forming surface of the receiver-amplifier chip toward the printed-circuit substrate. This mounting technology is used for mounting millimeter-wave band collision-avoidance radar chips, but by using it with the polyimide circuit substrate-based low loss transmission technology mentioned above, Fujitsu has successfully expanded the applicable frequencies into the terahertz band for the first time.

The use of this Fujitsu-developed technology will enable small devices to receive 4K or 8K HD video instantly, such as from a download kiosk with a multi-gigabit connection. It will also be possible to expand into such applications as split-second data transfers between mobile devices and split-second backup between mobile devices and servers.
In fiscal 2015, Fujitsu and Fujitsu Laboratories will begin field trials of multi-gigabit-per-second, high-speed data transfer using this newly developed compact receiver, aiming to commercialize this technology around 2020.