DVD Technical Guide
1. DVD History
Review Pages
2. Concepts and Structure of the DVD Format
3. The Future of DVD
4. Design Concept of the Physical Specification
5. Features of the DVD Physical Specification
6. The DVD Data Format
7. Read-Only Disc File Format
8. Video Format
9. Video Format - Page 2
10. Video Format - Page 3
11. Audio Format
12. Audio Format - Page 2
13. Audio Format - Page 3
14. Audio Format - Page 4
15. Audio Format - Page 5
16. DVD-R and DVD-RW
17. DVD-R and DVD-RW - Page 2
18. DVD-R and DVD-RW - Page 3
19. DVD-R and DVD-RW - Page 4
20. DVD-RAM
21. DVD-RAM - Page 2
22. DVD-RAM - Page 3
23. DVD-RAM - Page 4
The following Technical Guide is dedicated to the DVD format and its releated technologies. The guide was written from the R&D Department of Pioneer. You can find the article at Pioneer's official website here.
Chapter 1 - DVD Overview
1.1 DVD History
Pioneer began development of a new digital video disc format in 1991, with the goal of recording two or more hours of high-quality video on one disc, as a next-generation replacement for the LaserDisc.
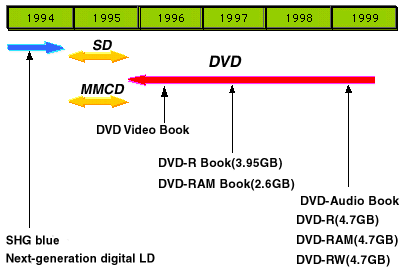
In 1994, Pioneer introduced to the market an industrial model called the ![]() Karaoke System, which could store and play back 2.1 GB of MPEG-1 data from a one-sided, 1.2 mm thick disc, using a 680 nm laser. In 1994, Pioneer also developed another digital video disc system which used an SHG blue laser. In response to Hollywood's desire to have this kind of new system enter the market before multi-channel satellite broadcasting, Pioneer worked with Toshiba to propose a disc specification called SD, which used a red laser, at the end of 1994. Around the same time, Sony and Philips were promoting the MMCD specification. The major difference between the SD and MMCD specifications were whether the discs should use two 0.6 mm substrates bonded together, or a single 1.2 mm substrate, as an extension of the CD format. At the end of 1995, agreement was finally reached on a specification that combined the two-substrate approach of SD with the 8/16 modulation of the MMCD specification. At this point the DVD Consortium was formed, and DVD truly got started.
Karaoke System, which could store and play back 2.1 GB of MPEG-1 data from a one-sided, 1.2 mm thick disc, using a 680 nm laser. In 1994, Pioneer also developed another digital video disc system which used an SHG blue laser. In response to Hollywood's desire to have this kind of new system enter the market before multi-channel satellite broadcasting, Pioneer worked with Toshiba to propose a disc specification called SD, which used a red laser, at the end of 1994. Around the same time, Sony and Philips were promoting the MMCD specification. The major difference between the SD and MMCD specifications were whether the discs should use two 0.6 mm substrates bonded together, or a single 1.2 mm substrate, as an extension of the CD format. At the end of 1995, agreement was finally reached on a specification that combined the two-substrate approach of SD with the 8/16 modulation of the MMCD specification. At this point the DVD Consortium was formed, and DVD truly got started.
In August 1996 the DVD Video Book was published, and the first DVD video players went on sale in November of the same year. The 3.95 GB Write-Once DVD-R Book, and the 2.6 GB rewritable DVD-RAM Book, were published in 1997. A DVD-RW Book and DVD-RAM Book, which define 4.7 GB rewritable formats, were published in 1999. A specification for 4.7 GB DVD-R was introduced in 2000. Two application specifications, the DVD Audio and the DVD Video Recording specification, were introduced in 1999. Following these specifications, DVD audio players, which provide high-quality multi-channel audio, and DVD video recorders, which allow recording to and playback of DVDs, were introduced to the market.
Review Pages
2. Concepts and Structure of the DVD Format
3. The Future of DVD
4. Design Concept of the Physical Specification
5. Features of the DVD Physical Specification
6. The DVD Data Format
7. Read-Only Disc File Format
8. Video Format
9. Video Format - Page 2
10. Video Format - Page 3
11. Audio Format
12. Audio Format - Page 2
13. Audio Format - Page 3
14. Audio Format - Page 4
15. Audio Format - Page 5
16. DVD-R and DVD-RW
17. DVD-R and DVD-RW - Page 2
18. DVD-R and DVD-RW - Page 3
19. DVD-R and DVD-RW - Page 4
20. DVD-RAM
21. DVD-RAM - Page 2
22. DVD-RAM - Page 3
23. DVD-RAM - Page 4